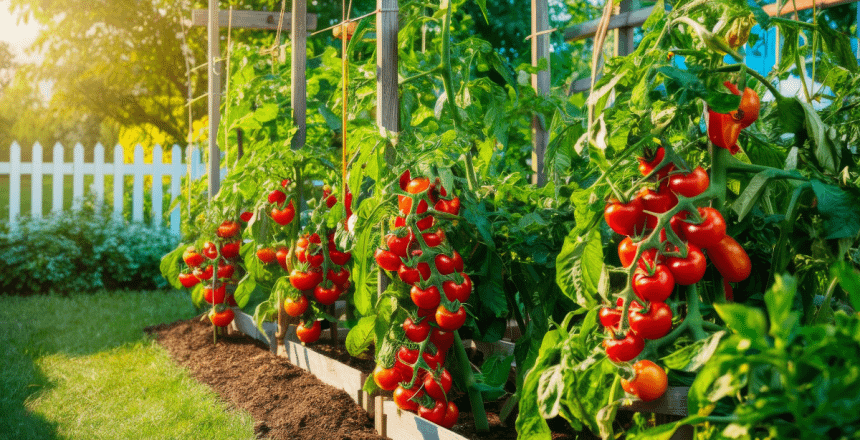
Cultivating vegetables at home is an inexpensive means of contact with nature. It saves money, improves the taste and freshness of food, and encourages active living. Food made from vegetables grown in the house is generally tastier and healthier than food bought from stores. Gardening also brings mental comfort, minimizes packing and transporting, and is eco-friendly. Additionally, it enhances self-sufficiency, allowing people to take charge of their food, and is useful for learning, allowing the individual to properly understand plants and food creation whilst deepening the bond with nature.
Choose The spot For your Garden

Selecting a place to set up your garden is one of the most important things to accomplish, as it determines your plants’ overall health and productivity. If the area is well chosen, there will be enough sun; hence, plants can carry out photosynthesis and grow in size properly. It also aids water movement by preventing puddle formation and root decay. Besides, picking a proper site permits the control of other factors, such as wind directions and storminess or boys’ hotness and coldness. Selecting the correct location serves the purposes of healthy plants, optimum yield, and simple gardening practices.
Sunlight
Photosynthesis is the key to success in the garden, as it is the process that allows plants to turn light and carbon dioxide into sustenance. Most vegetables do best when they receive 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily, although some plants do better in the shade. Consider the amount of sunlight in your garden, as well as where you will place the plants to get the most light. Some plants will manage in the shade, while others will be particular about the light required. Finding each in the garden determines whether enough light will be available. The plants can thrive and grow to their full potential, and the garden’s health is improved when sunlight is provided in the appropriate amount.
Convenient Water Access
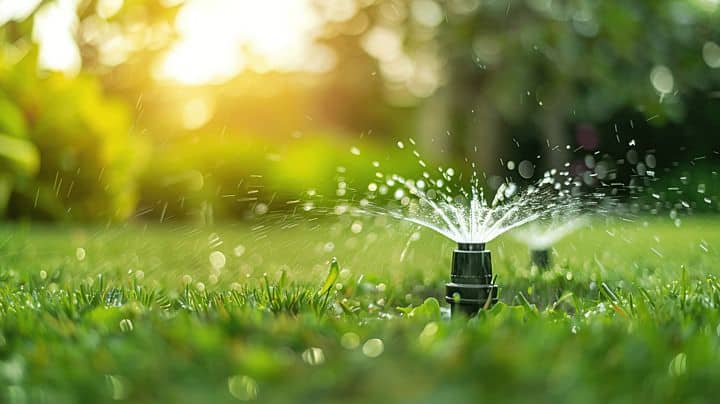
To facilitate the efficient flow of water, it is advisable to construct one’s garden close to the water source. Create channels with the goal of meeting your water needs as quickly as possible. This will spare you some effort and time, making working in the garden far less tedious. You might also think about installing a drip computer or using soak hoses so that less water can be wasted, water can penetrate deep into the earth, and the roots can grow healthily. With these systems in place, it is expected that the vegetable garden’s productivity will improve, and the basic structural development of the plants will be correct.
Proper Drainage System
When selecting a good spot for a vegetable garden, choose a site that is well-drained to avoid water logging, help prevent root rot, and even reduce the chances of developing fungal infections. Usually, sandy soil ensures proper drainage because water deposition is rapid, whereas clayey soil tends to hold too much water, making it unsuitable for plants. However, before deciding on a site, one should first go ahead and take a few inches off the ground and see the type of soil underneath. However, if the soil is heavy and predominantly clay, you can increase drainage by adding peat moss compost or perlite. Another method is to use raised beds or plants in mounds, which helps to improve drainage and soil quality.
Vegetable Garden Size

Yard size planning, as well as the amount of plants that are intended to be grown, determines the size of a home vegetable garden. It should be noted what size of family it is meant for or how much food waste one intends to collect. Think about how much food you need and how much effort you put into growing fresh vegetables. Additionally, different vegetables require different areas, so it’s important to consider the vegetables you wish to grow. Certain guidelines about the row layouts and spacing templates for the vegetable gardens enhance the yield. Considering these factors, you will be able to grow a successful, productive garden.
Primary Form
For those new to vegetable gardening, a suitable size is a garden that measures not more than 10′ x 10′ (100 square feet). Try initially limiting yourself to growing 3 to 5 sorts of vegetables and buying 3 to 5 plants of each selected variety. For a row-based layout, use a primary bed size of 4′ x 4′ or 4′ x 8′. This is a method of planting that yields a certain amount of produce while remaining within specific boundaries and requiring minimal effort.
Intermediate From
As you become more experienced in vegetable gardening, you will also want to expand the garden to an even larger space between 30′ x 30′ and 50′ x 50′ (900-2500 square feet). Within this larger space, one could easily grow 15 to 20 varieties of vegetables by planting 15 to 20 plants of each type. This enlarged vegetable garden will be enough to sustain a surplus for a family of four, with some leftovers for sharing or preservation.
Advanced From
For those who have enough land space and want to grow vegetables during all seasons, each family member will need approximately 200 square feet of space. You will certainly have enough food for your family to share and sell. This method ensures a wide variety of food and a plentiful supply throughout the year.
Preparing The Ground

To begin vegetable gardening, the first step is to remove the weeds and debris from the selected area. A hoe or rototiller can be used to loosen the soil, as this allows for the flow of air and drainage to be reinforced. Additionally, incorporating compost or any other organic fertilizer will improve the quality and structure of the soil. Also, smoothen the soil and prepare rows or beds for orderliness. If the soil is well prepared in advance, it has a good nutrient value and is well-drained, ensuring that plants grow healthier and yields improve.
Clearing the Area
Removing weeds and debris is a core principle of landscape preparation and planting gardens. First, clear your area of weedy plants, stones, and decaying parts of past plants, since these unwanted plants become competitors for nutrients and hinder the planting process. For more confined areas, such tools as a hand trowel, weeder, or hoe may be employed, while a shovel and rake will be sufficient for more extensive areas. Try to clear the site a few weeks before planting so that weeds that remain uncut will sprout out and then be cut off, creating a conducive and fertile area for the plants you will be planting.
Soil Preparation
To grow vegetables successfully, checking the soil pH and nutrients is crucial. To determine your soil’s pH and nutrient levels, use a sore test kit from a garden center; most vegetables will grow well in soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Introducing organic matter into the soil, such as compost or well-decayed animal waste, improves its fertility and moisture retention. Also, light tilling and management of the soil improve its drainage and ventilation. But beware of excessive cultivation, as it disturbs the soil profile.
Setting Up Boundaries
A fence is appropriate for protecting your garden from pets and other aggressors, such as rabbits and rodents, deer, and goats. Raised beds are a beneficial option for soil with poor quality or drainage since they facilitate better control of soil conditions and ease the pressure on one’s back during gardening. Moreover, garden borders are also used to create decorative edges around and within your garden (along borders or perimeters of the beds). They can be in the form of stones or wooden borders, which helps to beautify the garden.
Selecting Seeds and Plants

When planning a vegetable garden, pick the appropriate seeds and seedlings corresponding to the garden’s climate, soil, and area. Choose the varieties according to your country and time of year. Consider the most productive and disease-proof types. Think of your family and room. If you are a beginner, you need to start with simple vegetables and make sure that the seeds or plants are purchased from a reliable source.
Choosing the Right Vegetables
Remember to consider factors such as climate, spatial availability, and the individual’s liking when selecting the vegetables to grow in the garden. Grow vegetables that will thrive in your area’s weather conditions. Some are suited for cold climates, while others are for hot climates. Consider the size of the garden to avoid overcrowding, and ensure that every plant grows in an appropriate space. For a first-timer, radish, lettuce, and zucchini are some of the quickest and easiest vegetables to grow for their low cultivation and care demands. Furthermore, you must know the differences between heirlooms and hybrids of the same species when growing crops: the former are excellent tasting and traditional, while the latter are created specifically for some traits, such as pest resistance. Choosing between the two depends on gardening goals and preferences.
Sourcing Seeds and Seedlings
When it comes to getting seeds for your garden, there are several options. For example, as far as seeds are concerned, a local garden center is always a good option as it provides seeds appropriate for the area’s climate and soil. Online stores, on the other hand, offer a wider selection, but it is necessary to define and check the rating in order to avoid poor-quality seeds. Direct sowing is sometimes ineffective, and it is advisable to manage these plants indoors from seeds, especially with tomatoes, which have a long growing season. If you want an easier and faster method, you can purchase seedlings. Usually, the seedlings are ‘older’ and are ready to be planted in the garden, thus saving the time and effort needed for the vegetative stage.
Planting Your Vegetables

Each time you want to grow some vegetables, begin with soil preparation, which should be loose, rich, and well engraved. Plan the bed’s plant placement, leaving enough space for growth. They adhered to the guidelines for deeply planting seeds or seedlings. They drenched the planted area completely upon seeding to encourage the plants to root. Think about using mulch to keep the moisture in the soil and prevent weed growth. At intervals, check your garden and take care of it to achieve healthy vegetables.
Timing Your Planting
For every gardener, comprehension of the best seasons to plant various vegetables is vital. Vegetables do have planting requirements regarding temperature and frost dates. Therefore, local knowledge becomes crucial in determining when to plant the crop. Excellent organization practices can be enhanced by formulating the planting timetable, which shows when seeds are sown or when seedlings are transplanted. Also, local gardening calendars, which are commonly offered as extensions to older posts, contain important information about the specific weather conditions and periods for planting your vegetables. These resources will be advantageous for planning a successful crop yield throughout the year’s warm months.
Planting Techniques
The two types of planting depend on the plant: either directly sowing seeds in the garden or sowing them indoors and transplanting them later. Certain seeds do better when placed on the earth, whereas some are better off hibernating indoors before exposure to the external environment. In this way, overcrowding is prevented, reducing the competing factors for growth and disease risk. It is also advisable to strictly adhere to the spacing and planting depth specified on seed packets for optimal growth after germination.
Watering and Fertilization
Regular watering is critical for any garden’s proper growth. Generally, try to water about an inch per week, adjusting according to rainfall and plant needs. Organic alternatives such as compost are ideal for enriching the soil, but they are more effective in times of limited liquid fertilizer application. Knowing the types of fertilizers available and their purposes will ensure you use the correct method. Further, look for any effects of overwatering or lack of nutrients, such as yellowing leaves or plants wilting. Noticing these problems early enough will enable one to take corrective measures to improve the garden’s state.
Maintaining Your Vegetable Garden

To achieve the anticipated outcomes, maintenance should come after establishing a vegetable garden. Insects and diseases may attack vegetables, so it is prudent to detect this as early as possible—regular weeding and mulching help to prevent weeds and leave plants in excellent condition. With proper tending and care, you will be able to reap vegetable crops from the garden within a few weeks.
Pest and Disease Management
To maintain a thriving garden, you must inspect your plants from time to time for typical pests like aphids and slugs, as well as typical diseases such as blight. To avoid these concerns, use neem oil or insecticide soap beforehand and treat them simultaneously. Preventing the sources of pest annoyance is crucial. When pests or diseases become unmanageable or don’t seem to disappear with your attempts, visiting a local garden center or calling extension services could be the solution. Expert help provides guidance on how to provide adequate support in any gardener’s work.
Weeding and Mulching
Weed control is an important aspect of gardening practices. This is crucial because weeds consume the same nutrients and moisture as your plants. Treat weeding as a seasonal routine for a gardener. Placing mulch on top of the soil around your plants helps to keep it moist and suppresses weed growth, which is good for overall plant health. Planting ground cover crops during the off-season is also very helpful in maintaining and improving soil structure and preventing erosion, resulting in a good garden ecosystem.
Harvesting Your Vegetables
It is important to note that each type of vegetable has an acceptable degree of ripening, so you will find vegetables with optimal taste and texture. Understand the principles of the sturdy artisans and treat each vegetable with care. Still, proper harvesting and storage should be applied, since most vegetables will keep yielding if managed well. For those who love farming and enjoy harvesting vegetables, the author intends to put forward some measures to help you better manage your harvest. In a home garden, understanding the concepts of harvesting, appropriate storage, and proper maintenance is crucial for long-term enjoyment of the garden’s bounty.
FAQ
Which vegetables can a beginner gardener grow without difficulties?
The least challenging crops beginners can plant are lettuce, radishes, carrots, cherry tomatoes, and zucchini. These crops require little effort and tend to have a short growing season, which can suit most conditions; hence, they are ideal crops for starters.
When is the best time to start a vegetable garden?
When you want to initiate a vegetable garden depends on the climatic conditions of a particular region and the type of crops you intend to grow. Most container plants can be started in early spring, after the last freezing day and when the ground has warmed up. For vegetables to be harvested in the fall, planting should be done mid- to late-summer. For vegetables like haricot Chicago and peppers as such, the seeds can be started in the house during the 6–8 weeks before the last frost is expected.
Are there vegetables that can be grown in pots?
Yes, vegetables can be grown in pots. Use appropriately sized pots and good-quality potting mix, and choose dwarf or compact varieties. Pots are also good for small areas and are very portable.