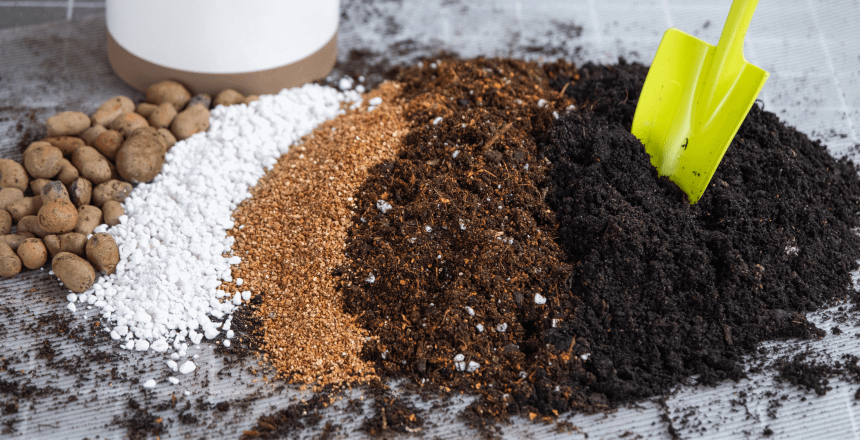
Soil amendments are essential for enhancing soil quality, which in turn improves plant health and growth. These amendments also help to reverse soil deficiencies and improve soil in a way that is optimal for root growth. Increased soil quality results in better moisture holding capacity and drains, as well as soil nutrient distribution, which promotes plant growth and increased garden productivity. Soil amendments also reduce chemical fertilizer use, making organic gardening even more possible. Such a change of focus to enhanced natural soils is able to support soil health and the environment over the long term.
Compost

Compost is a natural fertilizer that contains a mixture of organic matter and microbes to improve soil fertility and structure. It is made out of food waste, plant waste, leaves, grass, and other biological waste. During the composting process, these materials decompose into a nutrient-rich, dark-colored substance that resembles soil. Compost contains the primary nutrients and microorganisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi, that are beneficial for soil and plant growth. It is also a green technology that composts organic waste and improves soil structure.
Benefit Of Compost
Composting for gardening is a long-standing practice that continues to be beneficial. The benefits of composting are given below:
- Soil Health Improvement: Compost improves soil and nutrient retention, which is critical for plant growth on any given land.
- Nutrient Deficiency Recovery: Compost heals the soil deficiency by supplying the missing elements, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and as a result, making the plants tougher.
- Microbial Activity Stimulation: Compost allows more beneficial bacteria to thrive in the soil, improving nutrient accessibility and disease resistance.
- Reduces Waste: Composting answers the need to do away with organic rubbish like food waste or garden waste, which is helpful in landfills.
- Eco-Friendly & Cost-Friendly: Composting is not only eco-friendly but also cost-effective because it reduces the need for expensive artificial fertilizers.
Coconut Coir

Coconut coir is the fibrous part of coconuts, mainly used to enhance soil properties. It is available in two primary forms: coir pith and coir bricks.
This process begins with sourcing coconut husks, which are then immersed in water for four or more days in the vessel. After this soaking process, the husks undergo a cleansing and drying process. After they have been dried, they are cut into small pieces and pulverized into a dust-like product. This powder is used to enrich the soil, creating a suitable environment for growing crops.
Benefit of Coconut Coir
The following is an essential benefit of using coconut coir in the garden:
- Moisture Retention: Coconut coir material has excellent water retention properties, which helps maintain plant moisture levels without waterlogging.
- Soil Aeration: Its light and fluffy nature improves soil drainage and aeration, which in turn encourages root growth.
- Eco-Friendly: Coconut coir is a pleasant supplement for gardeners because it is made from natural, biodegradable substances.
- Improves Soil Structure: Coconut coir aids in amending the soil structure, which is important for the absorption of nutrients for plant health.
- Recycle: It is one of the products that can be reused, which helps the environment and reduces gardening waste.
Peat Moss

Peat moss is an organic matter made of decayed sphagnum moss and other flora in wetland areas, especially peat bogs. It has a sponge-like consistency and is known for holding water within its structure while also aiding in the aeration and drainage of soil. A horticultural ingredient extensively used in various forms, such as the soilless potting mix, peat moss facilitates the establishment of an optimum growth substrate for plants.
Benefit Of Peat Moss
Moisture Retention: This medium (peat moss) has excellent moisture-holding capabilities, which make it valuable during seed germination and maintain the moisture level for plants.
Sterility: Peat moss is prized because of its self-sterile nature. It inhibits plant pathogens and is a natural product made without chemicals. In this respect, it is of significant importance, especially to young or less resistant plants, as they can benefit from it. Furthermore, it retains moisture, so it serves as a soil enhancer, as well as making the soil light and porous.
Acidity: Peat moss typically has a pH between 3.5 to 6.0, making it effective at modifying soil acidity. It allows the growth of acid-loving plants, including strawberries, blueberries, azaleas, etc. Leveling of pH that is too alkaline in peat moss soil for agricultural purposes may also be a use for peat. It is effective in providing results, more often long-term and even short-term, in the growth of plants and also acts as a particular amendment in acidic soil conditions.
Hpynaceae Moss

Hypnaceae represents a broad family of mosses that are universal in distribution. They are members of the class Bryophytes, subclass Bryidae, and order Hypnales. Peat from the decayed bodies of the Hypnaceae dumps, such as Hypnum, Polytrichum, etc., is used in different mediums. Even though it changes pretty fast, it remains appropriate for gardening and other uses. Hypnum moss, in particular, creates a low-thickness, soft soil covering that is used for decorative purposes in stone placements. It is ideal for a location with light to moderate foot traffic.
Benefit of Hpynaceae Moss In lawn
The benefits of using hypnaceae moss in lawns are listed below:
- Improved Soil Structure: Hypnaceae moss promotes plant growth by increasing the soil’s moisture-holding capacity and aeration.
- Lush Ground Cover: Thanks to its compact growth, a soft green layer is readily available, which minimizes soil erosion and beautifies the environment.
- Low Maintenance: Offers a grass alternative, which requires less maintenance than traditional sod lawn.
- Resilient in Various Conditions: It thrives in a variety of conditions, ensuring that an attractive lawn is maintained for an extended period of time.
- Erosion Control: As a result of its vigorous and broad terrain strategy, soil erosion is quickly reduced.
Sphagnum Moss

Sphagnum moss is a species of moss that grows in wet areas, forming dense swamps and covering a thick area of soil. When soaked with water, sphagnum moss can swell up to 20 times its original size, which makes it an effective tool for enhancing soil moisture to the surface in agricultural fields. Sphagnum moss is used in horticulture to control fungal infections because of its antiseptic properties, especially in sterilizing potting mixtures.
Benefit Of Sphagnum Moss
Water Retention Efficiency: They do this by absorbing water, which is crucial in supporting growing plants. The aerobic conditions of sphagnum moss can, however, be useful in preserving moisture levels in soil and garden beds, even in water-scarce periods when re-soiling the areas frequently is impractical.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: It helps to hold important nutrients for growth so that when plants are hit by issues like drought, there is a backup. Also, sphagnum moss has follow-on benefits such as antibacterial and antifungal properties that aid plants in interaction with pests and diseases or the plants themselves.
Improved pH Balance: Naturally acidic, sphagnum moss can help lower the pH in areas where soils tend to be alkaline, thereby increasing the effectiveness of nutrient assistance. It also encourages less weight on the soil, resulting in increased air circulation, better drainage, general flooding, soil heat, and soil erosion and runoff.
Perlite

Perlite is a light, granular volcanic rock with a white appearance. When added to potting soil, it facilitates soil aeration while keeping it light and holding water. This is especially useful for crop production as it helps prevent overwatering of the plants so that the roots will not rot. Thus, perlite is an essential component in compost and soil mixes to help grow plants healthier and enable better seed germination.
Benefit of Using Perlite in Garden
The benefits of using perlite in the garden are given below:
- Improved Drainage: Perlite in the soil improves drainage, so excess water will quickly drain away and minimize water logging, which contributes to root rot.
- Increased Aeration: It also improves soil aeration to the roots by providing the required amount of oxygen for optimum growth.
- Reduced Compaction: Perlite helps keep the soil light and not too dense, allowing for easy root penetration, reducing soil compaction.
- pH Neutrality: Perlite is pH neutral, so the soils are quite well balanced and can support any type of plant.
- Disease and pest Resistance: It also, due to its sterility, offered protection from microorganisms and insect pests, which are mainly found in the soil, helping to enhance a better target for plant growth.
Vermiculite

Vermiculite is a mineral used in some processes to improve the soil’s quality. It is extracted from the subterranean, expanded, and then converted to extreme heat and pressure. This treatment produces a very light material with many small, air-filled particles. This is why vermiculite is added to potting soil, garden, and indoor plant mixes, as it improves soil water retention and enhances air circulation within the soil.
Benefit Of Using Vermiculite in Potting Mixes
Using vermiculite in potting mix has the following benefits:
- Moisture Retention: Vermiculite has wetter soil properties, and its moisture is easily retained when plants get water for long periods of time.
- Improved Aeration: Its lightweight and porous characteristics help increase oxygen expectoration in the soil, which promotes healthy rooting.
- Nutritional Retention: Vermiculite also aids in nutrient retention. As time passes, it releases some remains of soil minerals, making nutrients readily available to plants.
- Reduced Soil Density: It not only lowers soil density but also protects soil structure, making it useful for fresh plant seeds and potting mixtures.
- Long-standing Stability: Vermiculite does not decompose, which is long-lasting and doesn’t lead to degradation of the content in the potting mix over time.
Wood Bark & Chips

A horticulturist and landscaper would need tree bark and wood chips as organic materials in their work. Tree bark refers to the protective outer covering of a tree’s trunk and branches, whereas wood chips refer to small bits formed when large pieces of wood are chipped off or shredded. These materials improve soil health, beautify gardens, and serve functional purposes such as suppressing weeds and retaining water. Yet, raw wood materials also sequester nitrogen in the soil during the decomposition process, which may hamper plant growth.
Benefit Of Wood Bark & Chips for Landscaping
The benefits of using wood bark and chips in landscaping are given below:
- Soil Aeration: They prevent soil compaction and increase its pore space, thereby improving root development and water penetration.
- Moisture Retention: They reduce the evaporation of soil moisture, thus reducing the frequency of watering.
- Weed suppression: They prevent sunlight from reaching the soil surface, reducing weed growth.
- Temperature Regulation: They help to contain and regulate the moisture temperature in the soil, thus preventing the soil from drying out from excessive heat in the soil in winter months.
- Visual Appeal: They are visually appealing, making the landscaped garden beds and walkways stylish and prestigious.
- Soil Contamination: As the soil breaks down, they bolster it with organic material, increasing its fertility and structure.
Manure

Manure, an organic material made from animal dung, is used to improve soil fertility. It is primarily in the form of livestock feces from farm animals such as cows, horses, chickens, pigs, and is frequently combined with bedding material such as straw or sawdust. Such nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are incorporated into the soil and encourage plant growth. It also enhances soil features such as structure, moisture control, and microbial activities. For practical use, manure should be either composted or rotted so as to take care of the high nitrogen concentration that is usually detrimental to plants.
Using Manure on Lawns
The correct method of using manure on the lawn is given below:
- Choose well-aged manure: Fresh dung performs poorly, especially on grasses, since it enables them to burn. Thus, it is recommended that only dried cow dung be used.
- Spread evenly: Using a sieve applicator or a shovel, take a small amount of dung and uniformly sprinkle it over the lawn grass.
- Integrate with soil: To a small extent, the dung should be worked into the earth so as to assimilate some of this material and disinfect it from the foul smell.
- Water thoroughly: After the application of manure, water the lawn to assist in the release of nutrients and the disintegration of the manure.
- Apply during the growing season: Manure should be applied when the grass growth is making good progress, i.e., in spring or early fall. Also, rainfall should not fall within a week after the manure has been applied to avoid the chances of runoff.
Garden Lime

Garden lime is an additive that consists of compressed limestone or marble. It alters the acidity or basicity of the soil, making the acid more neutral. Besides making soils more alkaline, garden lime contributes to improving plant nutrient utilization as well as encouraging proper root formation by making the earth more conducive to the growth of plants. In addition, it aids in improving soil structure, which means improved airflow and water movement within the soil. Garden lime is used widely on lawns, vegetable farms, and flowers existing where soils are deficient in lime so as to help improve the growth of the plants.
Using Garden Lime on the Lawn
The primary reason for using garden lime is to raise the pH of acidic soils. Several lime application areas are used, including lawns, flower beds, and vegetable gardens. Here’s the process for applying garden lime to achieve optimum results:
- Test Soil pH: Before applying garden lime, test your soil pH level to determine whether it is necessary. Soil pH testing kits are available at most garden supply outlets.
- Choose the Right Lime: Choosing the right type of lime is important because it is determined by the type of soil and the pH results, such as ground limestone or hydrated lime.
- Determine the Amount: This entirely depends on the instructions on the lime package or on the needed amount indicated after testing the pH. Most estimate about 5 to 10 pounds of lime for 100 square feet; however, this is subject to change.
- Spread Lime: Use any broadcast spreader or manually apply the lime uniformly on the soil surface. For garden beds, crosshatch the areas with scoopers appropriately to ensure good distribution.
- Incorporate into Soil: Rake or soften the lime into the upper couple of inches of soil only so that it can be adequately worked in and not allow the lime to lie stubbornly on the soil surface.
- Water the Soil: Limes require an outward dispersion, and therefore, wetting the soil after lime application is necessary to quickly dissolve the lime and eventually put it into practical use.
- Avoid Over-application: Liming and frequency should always be balanced, as more lime than necessary will cause excess alkalinity in the soil, which is unfriendly to plants.
- Monitor and Retest: To determine whether the requirements have been satisfied, 1-3 weeks after the application, the soil pH should be cured and retested to confirm that it is within the optimum level for the crops grown.
What Soil Amendments to Avoid

Certain soil amendments should be avoided since they can have adverse effects on soil health and, subsequently, plant health. Here are some soil amendments to steer clear of:
Gypsum: The importance of gypsum in soil cannot be overstated in that it helps in soil compaction. It does not have any influence on so-called acid or alkaline changes. Also, when gypsum is applied on the farm, soil salinity increases, which decreases the quality of the soil and impairs crop growth. If there is too much salt, soil nutrient content will be imbalanced, affecting plant health. More efficient and less pond gypsum should be avoided, and soil improvement solutions should instead be sought.
Shred Rubber: It is widely recognized that shredded rubber, being an old rubber tire, is unsuitable for soil due to its high chemical content. These chemicals can leach externally or into the soil, making it less healthy or causing its nutritional value to be below average. In particular, toxic substances present in rubber will kill organisms in the soil and discourage plant growth. Therefore, the time spent shredding rubber will put the soil at risk. Other materials should be included when amending soils and gardening.
New Wood Chips: New wood chips can be detrimental to soil as they mostly take up nitrogen. When these wood chips are added to the soil, microorganisms cause them to rot. This is nitrogen-intense, and as a result, the microbes use up nitrogen in the soil. Consequently, the nitrogen content of the soil goes down, and there may not be enough nitrogen for plants. This shortage may impair plant development and health in general. To solve this problem, composted wood chips or odorless food surplus with nitrogen are recommended as dietary supplements.
FAQ
How do soil amendments influence plant growth?
Soil amendments improve plant growth by altering the texture, nutrients present, and soil pH. They add fertility to the soil and increase drainage, aeration, and moisture retention, creating a conducive atmosphere for root growth and nutrient absorption.
How often should soil be amended?
Amendments to the soil should, however, be done no more than once a year, preferably in spring or fall. Compost can be supplemented every 3–6 months. Depending on the pH level of the soil, we also apply lime every 2-3 years.
What is the soil amendment ratio?
A standard procedure is to apply 1-2 inches of compost and incorporate it into the upper 6-12 inches of soil. The application rates for lime are approximately 5-10 pounds per 100 square feet, which can be modified according to the soil textures and pH. Always follow specific guidelines for each amendment.