The zebra plant, native to South America and belonging to the Acanthaceae family, has the scientific name Aphelandra squarrosa. It is commonly grown indoors as a houseplant due to its unique green leaves with white stripes, which make it visually appealing and popular among gardeners. The highlight of this plant is its yellow flowers; when they bloom (usually in late summer or early autumn), the zebra plant bears long golden bracts that can be several inches long, with each plant having two to four bracts that can last up to six weeks. Indoor zebra plants grow slowly, reaching a maximum height of one to six feet and a width of one to five feet over their lifecycle. While zebra plants are usually grown as household plants, in warm regions, they can be grown outdoors, where their flowers attract hummingbirds and butterflies.
Zebra Plants Care
The Brazilian native zebra plant is a beautiful and attractive plant but behaves sensitively when grown at home. However, by providing the necessary nutrients and proper maintenance, these plants can easily and quickly be grown at home. If you want to nurture this delicate plant at home, choose a place with high humidity and temperature and ensure indirect sunlight. You can use moist and slightly acidic or neutral soil. Use a suitable pot that complements its graphic striped leaves, and keep an eye out for its signature golden bracts in late summer or early autumn. Regularly prune the leaves and apply seasonal fertilizers to maintain the plant’s normal growth.
Sunlight & Location
Indoors, zebra plants thrive best in shade or indirect light, reflecting their natural habitat under tree canopies in warm, humid climates. Provide them with 6 to 8 hours of indirect sunlight daily. Direct sunlight can scorch their leaves, while complete shade may inhibit flowering. East-facing and north-facing windows are ideal for optimal growth and blooming, though south-facing windows work if they don’t get direct sunlight. Zebra plants also thrive in tropical environments such as sunrooms (avoiding direct sunlight), bathrooms, and kitchens where humidity is higher. Keep them away from drafts and fans, and ensure they receive bright, indirect light for healthy growth.
Temperature & Humidity
Zebra plants require a warm temperature for optimal growth. Due to their origin, these plants thrive best in moderate temperatures. Indoors, they grow well at temperatures between 60-70 degrees Fahrenheit, and temperatures should not drop below 55 degrees Fahrenheit. Keep the plants away from entrance areas where air flows directly and from air conditioners.
Proper humidity is crucial for the good growth of zebra plants. Typically, they thrive in high humidity (70-80%). If the humidity level at home is low, you can use a humidifier to increase it. Regularly misting the leaves with water can also help keep them slightly moist. Additionally, you can place the plant on a tray filled with water and pebbles; as the water evaporates, it will increase the humidity around the plant.
Watering
Zebra plants require consistent moisture to keep their soil always damp, but caution is necessary because excessive watering can cause the leaves to wilt and lead to root rot due to waterlogging. Zebra plants can be watered every one to two weeks. Before watering, always check the soil. Insert your finger about an inch deep into the soil; if it feels completely dry, then it’s time to water. Water thoroughly until it runs out of the drainage holes. Use room-temperature purified water and always water from the bottom of the leaves, never from the top. Proper watering will help your zebra plant grow beautifully and maintain the beauty of its leaves and flowers.
Soil & Fertilizer
Zebra plants thrive in well-drained soil that ranges from neutral to slightly acidic. A high-quality potting mix, such as a blend of vermiculite, perlite, peat moss, and coco coir, ensures good drainage and supports plant growth. Additionally, periodically changing the soil and potting mix around the plant’s roots can promote growth and provide fresh nutrients. Aim to keep the soil slightly moist, avoiding it becoming fully wet or completely dry.
To maintain proper growth and encourage blooming, you can apply fertilizer to the zebra plant seasonally. During the spring and summer, water-soluble fertilizer can be applied every one to two weeks. In winter, when the plant is dormant, avoid fertilizing. Always use the correct amount of fertilizer, as over-fertilizing can damage the roots and leaves of the plant.
Pests Control
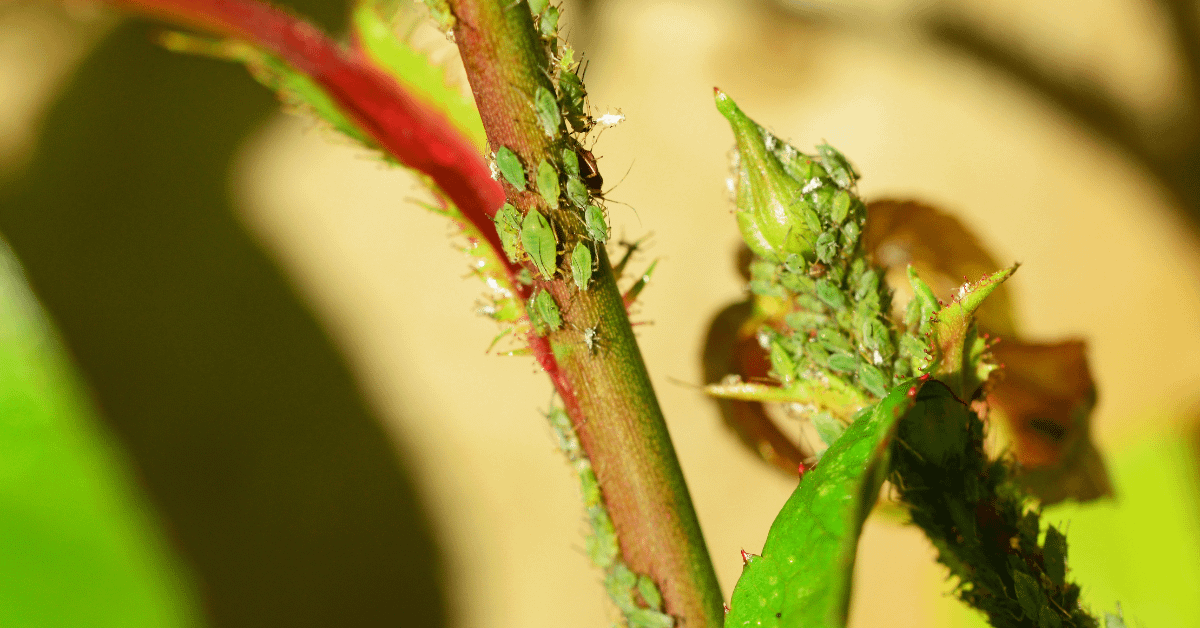
The attractive leaves of the zebra plant attract pests like aphids, mealybugs, mites, scale, and thrips. These pests sit on the plant’s leaves and stems, sucking the sap and excreting a sticky substance that creates yellow spots on the leaves. By regularly observing the plants, these pests can be identified and necessary measures can be taken to remove them. Initially, you can remove the pests with your fingers or a stick. Additionally, using soap water spray and neem oil can help remove the pests. If the infestation is severe, apply rubbing alcohol using a cotton ball or cloth on the pests.
Types Of Zebra Plants
If you want to nurture a small plant indoors, the zebra plant is an ideal choice. This plant is easy to care for and can be easily grown at home with minimal maintenance. It is known for its dark green leaves with white stripes and golden flowers. There are many variants of the zebra plant that can be easily grown at home and enhance the beauty of the house. Below are a few species of the zebra plant:
Dania
Aphelandra squarrosa ‘Dania’ is an attractive and elegant cultivar that originated from Denmark. Its green leaves feature white veins, and its stems are reddish-brown to maroon in color. The flowers are yellow and last for about six weeks. Like other cultivars of Aphelandra squarrosa, this cultivar follows the general growth and care requirements. It is relatively easy to care for and requires low maintenance. As an indoor plant, it is visually appealing and thrives well in a potted environment.
Fritz Prinsler
Aphelandra squarrosa ‘Fritz Prinsler’ originating from Germany, is the result of a cross between ‘Leopoldii’ and ‘Louisae.’ This hybrid Aphelandra plant features green leaves accented with slightly yellow veins, providing an attractive characteristic. This cultivar bears yellow bracts and flowers, which are visually appealing. Fritz Prinsler serves as an excellent indoor plant that requires low maintenance and can enhance the beauty of your home.
Snow White
Aphelandra squarrosa ‘Snow White’ is slightly different from other zebra plants. Its dark green leaves feature white veins and small white spots or specks near the veins and midrib, giving it the appearance of a snow-covered small succulent plant. The flowers of this plant are yellow and golden. Apart from the flower’s distinctiveness, the care requirements for this zebra succulent are the same, making it easy to maintain. As it grows, it often forms large clumps, enhancing its visual appeal.
Leopoldii
Aphelandra squarrosa ‘Leopoldii’ is known for its broad leaves, which feature classic white veins for a striking contrast. This cultivar grows from reddish-brown stems and bears golden flowers surrounded by red bracts. Its distinctive striped appearance makes it visually appealing. For indoor growth, it thrives in partially shaded areas, slightly acidic soil, regular watering, and seasonal fertilization. With low maintenance, this excellent indoor plant can easily enhance the beauty of your home.
Pruning For Zebra Plants
Pruning a zebra plant is essential for controlling its size, encouraging growth, and promoting flowering. Regularly remove dead, yellow, or diseased leaves to prevent the spread of diseases and enhance overall plant health. Pruning tall growth encourages the development of lateral branches, making the plant fuller and bushier. It also helps manage size and shape, making it more suitable for indoor spaces. For optimal results and to avoid damaging the plant, use sharp, clean pruning shears or scissors. The best time to prune is during the growing season, typically in spring or early summer. Regular pruning supports a healthy, well-shaped plant and encourages stronger and more frequent blooming.
Potting And Repotting For Zebra Plants
To grow a zebra plant at home, start by obtaining a suitably sized seedling from a local nursery. Choose a pot with drainage holes to prevent root rot. Prepare a high-quality potting mix by combining equal parts peat moss, perlite, and garden soil for good drainage and aeration. Place a drainage layer at the bottom of the pot, fill it halfway with the mix, then position the zebra plant in the center. Cover the roots with the remaining soil and lightly press to secure the plant. Water thoroughly and place the pot in a bright, shaded location.
Zebra plants grow slowly in pots and typically need repotting every one to two years. Repot when the plant becomes too large or roots emerge from the pot. The best time for repotting is during the growing season, usually in spring or early summer. Choose a pot that is one size larger with good drainage holes and use a well-draining potting mix, either designed for tropical plants or a blend of regular potting soil and perlite. Remove the plant from its old pot, trim any damaged roots, and add a layer of fresh potting mix to the bottom of the new pot. Place the plant in the center, fill around the roots with more mix, and water well to settle the soil. After repotting, position the plant in indirect sunlight to help it adjust and thrive.
Propagating A Zebra Plant
Propagating the Zebra Plant (Aphelandra squarrosa) is indeed a simple and effective method. Propagate the Zebra Plant by stem cuttings in the spring.The process of propagating zebra plant from leaf cuttings to create new plants is given step by step below:
1. Use a small pot that is at least 3-4 inches deep and fill it with a high-quality, well-draining potting mix, such as cactus or succulent mix.
2. With sharp, clean scissors or a knife, cut a healthy, green leaf, ensuring the stem is 2-3 inches long.
3. Allow the cut end to dry for several hours to a day to help prevent infection.
4. To promote faster root growth, apply rooting hormone powder to the cut end (optional).
5. Insert the cut end into the potting mix, about 2-3 inches deep, and gently press the soil around the cutting to keep it stable.
6. Place the pot in a bright, shaded spot and water the soil lightly to keep it moist, but avoid waterlogging.
7. Within about 2-4 weeks, roots should begin to develop. When new leaves appear, it indicates that roots are forming. Once the roots are established, transplant the cuttings into separate pots.
How TO Get Zebra Plant To Bloom
The Zebra Plant is known for its beautiful yellow flowers, but getting it to bloom can be challenging. It usually begins to flower in late summer or fall, and the blooms can last for about six weeks. To successfully encourage blooming, it is essential to first maintain the health of the plant.
Keep the plant in bright but indirect sunlight during the spring, as this helps promote flowering. In winter, place the plant in a cool location and move it to a warmer spot in the spring. After the plant has finished blooming, trim back the flower spikes to prepare the plant for the next blooming cycle. By following these care guidelines, you can increase the likelihood of regular blooming in your Zebra Plant.
Common Problems With Zebra plants
When growing Zebra Plants indoors, the leaves can encounter various problems and pests. Common issues include leaf drop, browning leaf tips, and curling leaves. These problems are often caused by overwatering, direct sunlight, and excessive fertilization. Below is a detailed discussion of Zebra Plant problems and their solutions:
Plant Leaves Falling Off
Leaf drop is a common problem for Zebra plants. Overwatering or underwatering can cause the plant’s leaves to fall off. Avoid making the soil too dry or too soggy. Check the soil and water it when it has completely dried out, ensuring that you water until the soil is thoroughly soaked. Additionally, low humidity can also cause leaf drop. If the air around the plant is very dry, increase humidity. You can use a humidifier or lightly spray the leaves with water to boost humidity.
Brown Leaves
Zebra plant leaves can turn brown due to direct sunlight, over-fertilization, and overwatering. Direct sunlight can scorch the leaves, so keep the plant in indirect light. Over-fertilization can also cause browning; fertilize moderately every 1 to 2 weeks during the growing season and avoid fertilizing in winter. Overwatering can lead to waterlogging, damaging the roots and causing browning. Water only when the soil has dried out and reduce watering in winter.
FAQ
How long does a zebra plant live?
A Zebra Plant can typically live for 3 to 5 years with proper care. Under ideal conditions, such as appropriate watering, light, and temperature maintenance, it can live even longer. Regular care and prompt resolution of issues help extend the plant’s lifespan.
Can zebra plants grow outdoors?
Zebra plants typically thrive indoors due to their preference for warm, humid conditions and sensitivity to direct sunlight. If grown outdoors, they should be placed in a shaded or partially shaded area, protected from cold temperatures and extreme weather, to ensure their health and growth.
Do zebra plants live in large pots?
The Zebra Plant can thrive in a slightly larger pot, provided it has good drainage and the soil is appropriate. A larger pot allows for more root growth, helping the plant become healthier and stronger, and can encourage flowering. However, avoid using an excessively large pot, as it may cause water to accumulate, potentially damaging the plant’s roots.