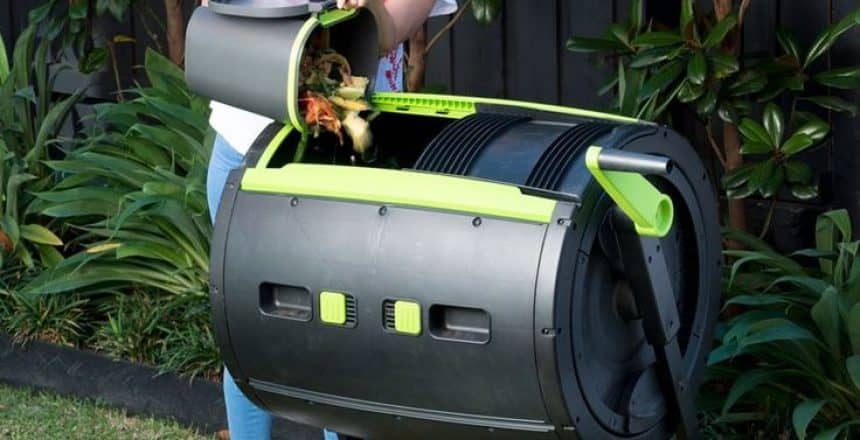
To start composting, a compost bin is essential as it maintains the proper moisture and airflow necessary for producing compost materials that enrich the soil. A compost bin enhances the composting process by ensuring the correct temperature and airflow for successful composting. Depending on the amount of compost you need for your garden and the available space, you can choose the appropriate size of a compost bin. Compost bins made of plastic, wood, metal, and other durable materials are available, but plastic compost bins are comparatively lighter and easier to use. For composting, adding green and brown materials, which are household waste items, is necessary. With regular care and proper procedures, compost can be obtained within a few days.
What Is Compost Bin
A compost bin is a sealed container or vessel where organic and easily decomposable materials are collected and transformed into compost in a clean manner. Compost bins are typically enclosed to prevent pests like flies, rodents, and odors from spreading. These containers are specially designed to ensure proper airflow, temperature, and moisture, facilitating the decomposition of organic or other materials.
How To Choose A Compost Bin
When choosing a compost bin, consider your available space and composting needs. Select a suitable bin for either outdoor or indoor use, ensuring it provides adequate airflow and drainage. Choose a bin that aligns with your composting volume, maintenance preferences, and specific environment and goals.
Indoor & Outdoor Compost Bin
Using a compost bin, whether outdoors or indoors, offers various benefits. If there is not enough space outside, an indoor composter can effectively manage kitchen waste and can be placed on the countertop. For outdoor composting, options include tumbling bins, in-ground bins, stationary bins, and vermicomposting bins. Each option has its advantages, so choose according to your space and preferences.
Size Determine
It’s important to choose a compost bin that isn’t excessively large or too small. Consider the amount of organic waste generated per week when selecting a compost bin, ensuring it can properly accommodate your materials. Tumblers and most indoor composters are suitable for small amounts of materials, making them ideal for limited spaces. If you need a larger compost bin, consider options like multiple stationary bins, a large food waste digester, or a tumbler with dual chambers.
Timeframe
When making compost, it’s essential to consider your patience and limitations. If you prefer to produce compost quickly and have limited space for long-term decomposition, choose a compost bin that allows for active composting methods. This way, you can expedite the process and create a small batch of compost using active composting techniques.
Types Of Composter
Various types of composters are available for making compost. Dry composters typically mix compost with soil. Stationary composters remain fixed and are usually suitable for outdoor use. Tumbler composters offer the advantage of rotation, aiding in faster compost production. Worm composters use worms to create compost quickly and efficiently. Each type of composter has its own size and method.
Dry Composter
A dry composter is a composting system that creates compost by mixing materials with soil or through atmospheric conditions. It typically uses dry substances like fallen leaves, dried grass, wood chips, and other dry materials. The dry composting process requires little to no water, allowing materials to decompose naturally and gradually to produce compost. You can create a DIY composter using a cardboard box or plastic storage container, which are easily available and can be repurposed as compost bins. Composting provides an eco-friendly waste management solution and a natural method for managing organic materials.
Stationary Composter
A stationary composter is a fixed composting system placed on the ground where compost materials are kept in one location to decompose. It typically operates in a closed, open, or semi-closed system where compost ingredients break down and decay over time. This type of composter is usually large in size and does not require regular mixing or cleaning of materials. It efficiently produces large quantities of compost and is generally used outdoors.
Tumbling Composter
A tumbling composter is a rotating composting system designed to produce compost quickly and evenly. Typically cylindrical or drum-shaped, it operates with a handle or lever for rotation. Tumbling the composter mixes the materials and increases oxygen flow, speeding up the composting process. Available in various sizes to suit different needs, it is ideal for home gardens. After adding organic materials, water, and rotate the composter regularly. Once it is three-quarters full, stop adding new materials but continue rotating. Compost can be ready in six to eight weeks, offering a clean and easy-to-use solution for composting.
Worm Composter
A worm composter is a system for composting organic waste with the help of worms. It typically consists of a container or bin where worms, such as red wigglers, process food scraps and other organic materials. The worms break down these materials into nutrient-rich compost known as worm castings. Worm composters are often compact and designed for use indoors or outdoors. They include features for drainage and aeration to maintain the right environment for the worms. This method of composting is efficient, producing high-quality compost quickly while also reducing kitchen waste.
Subterranean Composter
A subterranean composter is a composting system placed directly in the ground. It consists of a container or chamber buried underground, where organic waste decomposes naturally. The composting process is accelerated by soil microorganisms and natural temperature control, making it a space-efficient option that integrates well with the soil. These composters allow fresh air to circulate and protect against environmental factors such as excess rain and dry conditions. They include vents that enable worms and other beneficial microbes to freely enter and exit, which is crucial for the composting process.
What Items To Compost
You can use various types of organic materials to make compost. Both green and brown waste materials from households are used in composting. Here is a list of suitable materials for composting:
- Fruit and vegetable scraps: Including peels, cores, rinds, and seeds.
- Coffee grounds and filters: Used coffee grounds are excellent for composting.
- Tea leaves and tea bags: Ensure tea bags are made of natural fibers without staples.
- Eggshells: Crushed eggshells add calcium to the compost.
- Nutshells: Such as peanut shells, as long as they are not treated.
- Grass clippings and leaves: Green materials like these provide nitrogen.
- Straw and hay: These are good sources of carbon for the compost.
- Shredded paper and cardboard: As long as they are free of glossy coatings.
- Wood chips and sawdust: Ensure they are untreated and from non-toxic woods.
- Houseplant trimmings: Small prunings and dead leaves.
- Dryer lint: From natural fibers like cotton and wool.
- Hair and pet fur: Ensure they are free of chemicals and treatments.
- Wood ashes: In small amounts, as they raise pH.
- Old spices and herbs: Past their prime or unused.
- Manure: Only from herbivores and aged properly.
Avoid composting meat, dairy products, oils, fats, and diseased plants. Properly managing your compost bin with the right balance of green (nitrogen-rich) and brown (carbon-rich) materials will help you create nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
How To Make Compost
If you have a compost bin and a suitable location for composting, you can start the process. Begin by adding essential green materials like fruit and vegetable scraps, and brown materials such as eggshells, cardboard, coffee grounds, and dry leaves. These materials provide nitrogen and carbon, which are crucial for the composting process. Avoid adding oils, butters, fats, or any animal or fish parts to the compost bin, as these can create unpleasant odors and attract pests.
For successful composting, ensure that the compost bin has good airflow and temperature control. Regularly add moisture to keep the compost slightly damp, but not soggy. Turn the compost every two to three weeks to help mix the materials and improve aeration. This helps to speed up decomposition and prevents the compost from becoming compacted. With consistent monitoring and maintenance, you can expect to produce high-quality compost within two to three months. Additionally, keeping track of the compost’s temperature and adjusting moisture levels can further enhance the efficiency of the composting process.
How To Clean Your Compost Bin
Once composting is successfully completed, use the produced compost in your garden. It is essential to clean the compost bin before starting a new batch. The steps for cleaning the compost bin are as follows:
1. Empty the Bin: Once your compost is complete, remove all compost materials from the bin and empty it.
2. Prepare Cleaning Solution: Create a mixture using baking soda, a safe dish soap, and cold water. This mixture will be used to clean the compost bin.
3. Clean the Bin: Scrub the bin thoroughly with a bamboo brush or a stiff brush to remove all dirt and residual materials. A soft cloth or sponge can also be helpful.
4. Rinse and Dry: After cleaning, rinse the bin thoroughly and place it in an open area to dry. If possible, let it dry in sunlight to help kill bacteria and fungi.
5. Inspect the Bin: Check the lid to ensure it seals properly. Also, look for any damage to the bin, such as cracks, holes, or rodent bites, and repair as needed.
6. Add New Compostable Materials: Once the bin is completely dry, start adding new compostable materials. Before adding new materials each time, mix the old materials and fluff them well to improve airflow.
Benefit Of Compost Bin
The compost bin creates compost through the decomposition of organic materials, which improves the health of the soil. Composting methods supply natural materials to the environment and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers. Compost provides nutrients to the soil and creates an improved environment for microorganisms. Compost bins help conserve water in the soil and assist in good drainage. The use of compost bins enhances the beauty of your home and garden and helps store carbon, creating a healthy environment.
Waste Reduction
Using a compost bin reduces household waste. Organic kitchen waste, such as vegetable scraps, fruit peels, and tea leaves, can be thrown into the compost bin. This decreases the amount of trash and household waste, which has a positive impact on the environment. Additionally, this waste material can be used to produce nutrient-rich compost.
Soil Fertility Enhancement
Compost produced from a compost bin increases soil fertility. Adding compost to the soil enhances its nutrient content, thereby improving plant health and growth. It also increases the soil’s water retention capacity and air circulation. Mulch created from compost around plants helps protect them from various pests and physical damage.
Environmental Conservation
Using a compost bin helps conserve the environment. When household waste is indiscriminately dumped, it decomposes and pollutes the environment, releasing greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Composting household organic waste in a bin reduces the emission of these gases, which has a positive impact on the environment.
Cost Savings
Composting can save money. Commercial fertilizers are often expensive, but a compost bin allows you to produce your own organic fertilizer at home. This eliminates the need to purchase additional fertilizers. Compost retains moisture in the soil, reducing the need for frequent watering, thus conserving water and lowering irrigation costs.
Disease Prevention in Plants
While chemical fertilizers can increase crop yield, they can have adverse side effects, potentially degrading soil quality over time. Compost, however, has no such negative effects. It improves soil health and boosts plant disease resistance. The nutrients in compost strengthen plant roots, making them more resilient to diseases and pests. Additionally, compost fosters the growth of beneficial microbes and earthworms in the soil, enhancing soil structure, fertility, and biodiversity, which in turn promotes healthier plant growth.
FAQ
What should you put at the bottom of a compost bin?
At the bottom of a compost bin, place coarse materials like small branches, straw, or dried leaves. These materials aid in airflow and drainage, helping to prevent the bin from becoming too soggy. You can also add a layer of cardboard or paper to absorb excess moisture and further enhance aeration.
How to protect your compost bin from pests?
To protect your compost bin from pests, use a tight-fitting lid and avoid adding meat, dairy, or oils. Regularly turn the compost to aerate it and consider using pest-repellent materials like crushed eggshells. Maintain proper moisture levels and ensure good drainage to help prevent attracting pests.