Orchid plants rank highly among the most common house plants because of their bright and various flowers, which are found in pink, red, blue, and yellow, among others. Most orchid plants can reach one to three feet, with flower spikes ranging from 6 to 12 inches. There are an estimated 25,000 species of orchids, some of which are very common, such as Orchidaceae, Cattleya, Dendrobium, and Cymbidium. People mainly love these plants because they remain in bloom for quite a long time and add beauty to the surroundings, which facilitates the addition of such plants in the home interior.
How To Care For Orchid

Caring for orchids is relatively simple and less demanding than other houseplants. Orchids grow best in bright, indirect light, and moderate temperatures are ideal. Orchids require high humidity and adequate drainage. Avoid overwatering and only water when the soil is dry. With proper care and maintenance, these plants will provide long-lasting beauty and enchanting ambiance to the indoor bed. Here are some tips on how to cultivate orchids:
Location & Sunlight
For orchids to bloom, they need bright, indirect light—about six to eight hours per day. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can scorch the plants. Place the orchid near an east or west-facing window for moderate light, or near a south or west-facing window for bright light. If the light is too intense, use a light-blocking screen to protect it.
Soil & Fertilizer
Potting mix, or potting medium, is an essential ingredient for orchid growth. It should be light and drain quickly. Adding ingredients like vermiculite, coco coir, and perlite to the potting mix helps increase drainage. For orchid-growing media, slightly acidic soil with a pH of around 5.5 is ideal.
Fertilizer application is essential for orchid growth. You can use a balanced fertilizer with little to no urea for your orchid. Additionally, you can mix the fertilizer with water to make a liquid solution and apply it to your plants. You can fertilize your orchids once a week during the growing season. To prevent the plant roots from burning, thoroughly soak the medium before applying the fertilizer.
Watering
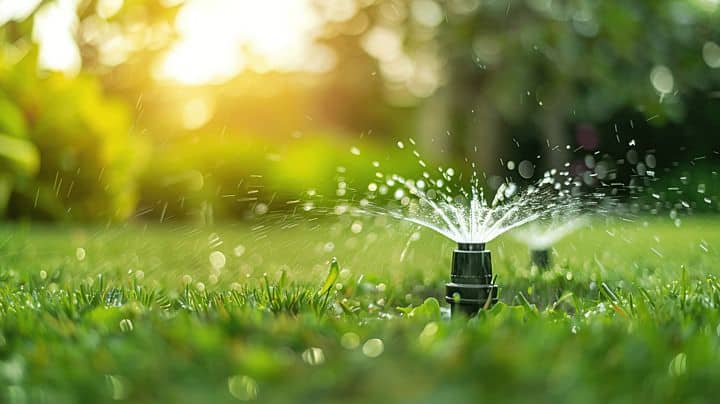
Regularly water orchid plants based on their requirements. Too much or too little watering can lead to orchid death. Once your potting mix begins to dry, gradually water your orchids until the growing medium becomes saturated. Orchid plants need more water in hot weather, so you can water them once or twice weekly. Water requirements significantly decrease during the cold season, and it’s best to water them once every two weeks.
Temperature & Humidity
Orchids are often grown in warm conditions. However, orchids cannot withstand exposure to intense sunlight or extremely low temperatures, as it could lead to their death. Warm days maintain a temperature range of 60°F to 80°F, which orchids find comfortable. Likewise, the plant will grow well on cold days under temperatures between 50°F and 70°F.
To develop and bloom steadily, orchids require regular watering and humidity replenishment. Most orchids have excellent humidity conditions. Apart from those values, a humidity level between 40% and 70% is acceptable, but going a bit over will help them grow even more efficiently. Suppose you want to maintain humidity levels for your orchids during the dry seasons. We recommend applying humidifiers or directly wetting the leaves to increase misting levels in that case.
Types Of Orchid Plants

Out of the roughly 30,000 wild orchid species, we have registered over 100,000 hybrid orchids, which primarily vary in terms of breeding methods, flower dimensions, color, and plant height. Crossbreeding different orchid species gives birth to hybrid orchids, and they are known for their vast and colorful flowers. Here is a list of these beautiful orchids you can choose from to add more aesthetic value to your home decor. These beautiful ornaments can help you enhance the beauty of your house. Here are a few popular types.
Moth Orchid (Phalaenopsis)
The moth orchid is a common orchid that blooms in the house. The plants bloom profusely on arching stems with many small flowers, each of which can remain open for two to three months. These orchids prefer bright and indirect light, so you can use the east window for them.
Cane Orchid (Dendrobium)
Cane orchid is one of the larger groups in the orchid family, with over 12,000 species. They produce flowers of a variety of shapes and colors, ranging from white to blue, as well as other colors. On each leaf of the plant, you will usually find flower clusters. Typically, these orchids range in size from 10 to 50 inches. Dendrobium orchids are one of many species in the vast orchid family, and they are among the most widely collected by orchid enthusiasts, garden centers, and botanical gardens. They are culturally diverse and broad in numbers.
Corsage Orchid (Cattleya)
The corsage orchid is one of the most famous varieties, known as the “Queen of Orchids.” These orchids possess beautiful, scented flowers with a fantastic variety of shapes and colors based on the species. They prefer plenty of light, a specific blend of nutrients, and lots of moisture. These orchids can range in height from 3 inches to a mammoth 24 inches.
Boat Orchid (Cymbidium)
Boat orchid is an attractive species that can grow in cold environments (10 °C). The orchids can bloom for three to four months. Among orchids, these plants produce relatively large flowers, which can be white, green, yellow, purple, and red. These orchids can range from 4 to 24 inches in height.
Pruning Orchid

Orchid pruning is a critical process that helps this beautiful and tender plant maintain its overall health and beauty. Plants are encouraged to bloom the following season by removing dead or wilted stems, pruning diseased roots, and cutting flowers afterward. Proper pruning prevents diseases and protects against a variety of infections and insect attacks. Use sharp and clean scissors or pruning shears to prune the orchid. If necessary, sterilize equipment by dipping it in alcohol to avoid contamination.
Propagating Orchid Plant

Propagation of orchids from seed is a complex process because seed sizes are small and the conditions required for seed germination cannot be met indoors. Division is the easiest and most effective method of orchid propagation. Here are the steps for propagating orchids using the division method:
1. Remove the orchid from its pot and carefully split up the root ball to win it out, making sure that each resulting division contains a minimum of three pseudobulbs or stems.
2. Cut or divide the clumps using sterilized scissors.
3. Place each division in a fresh pot with the new orchid medium.
4. Care for the divisions as you would individual plants, watering dormant divisions only when necessary.
Potting and Repotting Orchid

The best time to potting and repotting an orchid plant is during the growing season (spring or summer), avoiding winter. Orchids must be repotted for numerous reasons: they revitalize the medium, promote more oxygenation and better drainage, and minimize root loss while enhancing their growth. The plant has space to grow and is freed of its old, depleted media. To control pests and diseases, keep the process in check over time, which may be a key to improving plant health, leading to healthier blooms and better-developed plants.
Potting
When potting an orchid, choose a pot with holes that allow water to flow. A potting medium, such as orchid bark and chips, will demonstrate that your orchids have adequate air circulation and drainage. Add some medium to the pot, then center and position the orchid so its roots are in the middle. Rather than filling the pot to the brim with medium surrounding the orchid, fill it sparingly, as this will ensure airflow. After potting the orchid, lightly water it and move it to an area with adequate air circulation and light.
Repotting
Repotting orchids is generally recommended every 1-2 years, or whenever the potting medium wears out. Repot into a pot with drainage holes, and adjust it to the plant’s size. Unpot the orchid, remove as much of the old media around its roots as possible, and cut away any nasty/moldy parts. Add some new medium at the base of the new pot, then place the orchid in the middle and fill it around with fresh media. Avoid overpacking it because you want the press to be somewhat loose for air circulation. After finishing the report, thoroughly wet the soil with water and relocate the pot to a bright spot.
How To Get orchid To Bloom & Re-Bloom

Orchid plants bloom at least once or twice a year, and flowering times vary among orchid species. Its kidder flowers can last for an average of two to four months. Some orchids may not flower indoors, but phalaenopsis can bloom by lowering the temperature for several nights. Insufficient light is one of the main reasons orchids do not bloom. Orchid leaves have a light green color when they receive proper light, and too much light can cause orchid leaves to turn yellow and brown. By looking at the color and structure of the leaves, you can arrange the lighting needed for the orchid. When the orchid flowers wither, cut the stems with a sharp pruner; this will encourage the production of new flowers the following season. Furthermore, you can promote flowering by keeping quiet plants in a bright, shady spot, providing water and nutrients, and conducting regular monitoring.
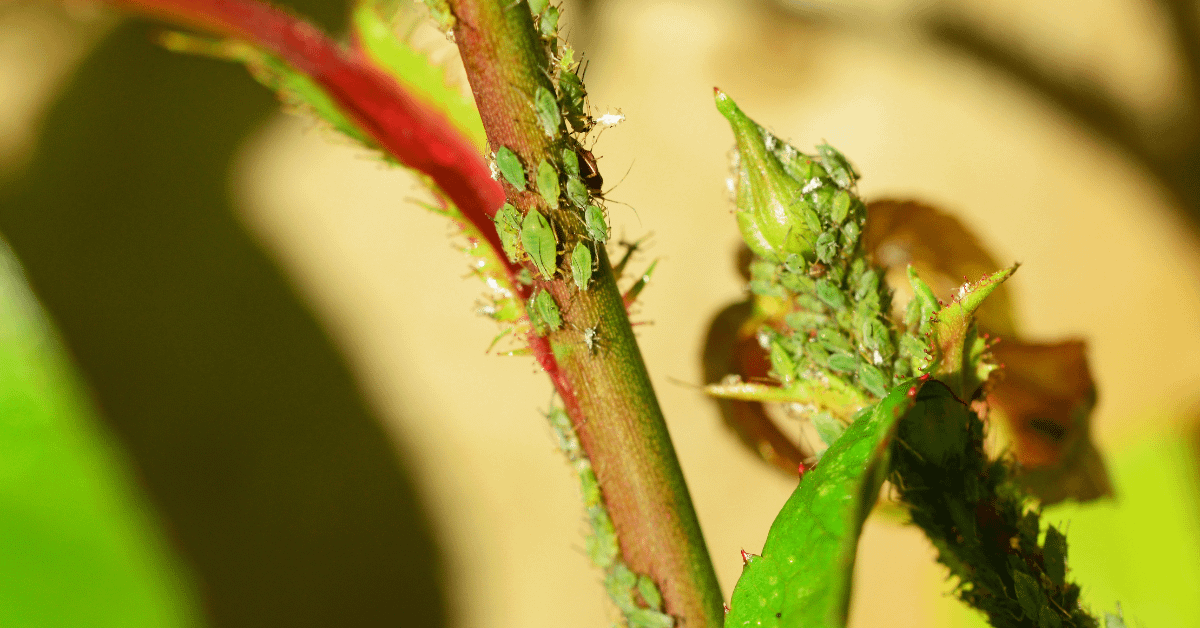
Common Pests And Plant Diseases

Indoor orchid plants are susceptible to pests and fungal diseases. It can hamper their growth and reduce flower production. We can resolve issues by identifying the problems and taking appropriate action. Here are some common orchid problems and solutions:
Pests Control
Pests such as mealybugs, spider mites, fungus gnats, aphids, and whiteflies can be attracted to orchids. Here is a quick guide to dealing with those issues:
- Mealybugs: Tiny, white, cottony clumps destroy new growth and produce sooty mold. Wash them away with soap and water.
- Spider mites: These small insects cause stippling and webbing on leaves. Increase the humidity and break out the insecticidal soap.
- Fungus Gnats: Tiny, dark flies with larvae that damage roots. Allow the soil to dry in between waterings.
- Aphids: small green or black insects leading to leaf distortion. Soap, water, or Neem oil use.
- Whiteflies: Tiny insects that cause yellowing and leaf dropping. Use insecticidal soap or Neem oil.
Plant Diseases
Overwatering orchids can cause root rot and the spread of various fungal diseases, including anthracnose (brown/black leaf spots), phytophthora (black spots, root rot), botrytis (gray/brown spotting on flowers), leaf algae (green/white growths on leaves), and petal blight (brown/black spots). There are several ways to prevent and manage these problems:
- Before watering, wait until the ground is dry to the touch.
- Clean the plant and remove any sick parts as soon as possible.
- Use appropriate pesticides.
- To reduce humidity and minimize disease development, allow for good air movement.
Common Problems With Orchids

When growing orchids, you can run into many problems, including dry leaves, yellow leaves, drooping leaves, and flowers turning yellow or brown. Overwatering, water stress, and not enough sun are the root of most problems. Effective solutions to these problems can be taken at the right time and in the right direction.
Dry and Wrinkled Leaves
The main causes of orchid leaves drying and curling are insufficient water and too much sunlight. If the leaves are not getting enough water, they will dry out and fade, so check the soil regularly and provide water. In addition, if the plants are under direct sunlight for a long time, the leaves are damaged and gradually dry up. Orchids grow best in indirect sunlight, so keep the plants in a bright, shady spot rather than in direct sunlight.
Yellowing Leaves
Overwatering is the leading cause of yellowing orchid leaves. Overwatering causes plant roots to become waterlogged, leading to prey death and leaf yellowing. For orchids, use a well-draining pot to drain excess water and allow air circulation to the plant’s roots. If the problem is more severe, remove the orchid from the pot, trim the damaged roots, and repot using the new potting medium.
Drooping Leaves
Orchid leaves may droop due to lack of sufficient water. Orchids generally grow best in high humidity, so water the plants regularly. When the soil’s surface is arid, continue watering until it is completely soaked. Additionally, a lack of light can cause orchid leaves to droop. So, provide orchids with bright indirect sunlight and avoid direct sunlight.
FAQ
How long does an Orchid flower last?
Orchid flowers generally last from 6 to 10 weeks, depending on the variety and care conditions. Phalaenopsis orchids can have blooms lasting about 8 to 12 weeks. Factors such as the temperature and humidity of the surrounding air, light exposure, watering practices, etc. affect bloom longevity. By simply taking proper care of the flowers, I can avoid this and enjoy them for a bit longer.
What are the signs of a healthy Orchid?
A healthy orchid’s leaves are firm and dark green, indicating proper moisture and light. The flower spikes will remain solid and straight, looking bright and fresh. Also, insects will not attack a healthy orchid, and the plant will show an increase in new leaf and root development over time.