Philodendrons are prized by gardeners for their variegated foliage, with hundreds of species within the genus displaying leaves of various shapes and colors, with deep shades of green being common. They are popular as houseplants because of their heart-shaped leaves and easy maintenance. There are generally two types of philodendron plants, some species produce flowers and grow in clumps while other species have beautiful heart-shaped leaves and do not produce flowers. These trees are typically 6 to 72 inches tall and 6 to 36 inches wide. Providing adequate water, the right temperature, and well-drained soil makes philodendrons relatively easy to grow indoors.
How to Grow Philodendrons
Philodendron plants can be grown in indoor environments with minimal maintenance. They require proper care for optimal growth. Philodendrons require bright light to ensure proper leaf color. Moderate water supply and well-drained soil enable plants to grow properly. By controlling factors such as temperature, soil quality and fertilization, you can ensure the proper growth of philodendrons in your home. Let’s discuss in detail how to grow philodendron indoors by controlling things like temperature, soil and fertilization:
Location & Sunlight
Philodendron plants like bright light because of their origin in warm countries. Sunlight requirements vary between different species of philodendron. Varieties with colored leaves need bright sunlight to maintain proper color. Direct sunlight can be harmful to philodendron plants, causing their leaves to burn. To provide bright sunlight, you can place your plants near a balcony or window in the northwest corner. If your plants get direct sunlight, consider applying a filtering process. Therefore, selecting a suitable location with adequate light is essential for the proper growth of your philodendron plant.
Soil & Fertilizer
Philodendrons thrive in slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5, enriched with organic matter. The soil should be loose and well-draining to prevent water from pooling around the roots, which can lead to root rot. An ideal growing medium can be created by mixing potting soil with vermiculite, perlite, and coconut coir. Adding organic compost or aged bark further enriches the soil, enhancing its nutrient content and promoting healthy growth.
Regarding fertilization, Philodendrons require feeding according to their growth cycle. During the active growing seasons of spring and summer, apply a balanced liquid fertilizer once a month. Choose a fertilizer with an equal ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (such as 10-10-10 or 20-20-20) and one specifically designed for foliage plants to support their lush, green leaves. For a more controlled release of nutrients, slow-release fertilizer granules are also effective.
Watering
Water is an essential element for plants. Philodendrons prefer moderate watering, allowing the top one to one and a half inches of soil to dry out between waterings. In warmer months, watering once or twice a week may be recommended, but in colder months, watering should be done once every two weeks. Remember not to overwater your plants. Excess water causes leaves to turn yellow and roots to rot. It is recommended to use distilled water to avoid any problems related to the presence of salt in your water. If the water used is high in salt, the plant’s leaves may turn yellow or brown. Therefore, maintaining proper room temperature and using distilled water is recommended.
Temperature & Humidity
The right temperature is very important for philodendrons as they naturally prefer warmth and humidity. The temperature and humidity requirements for different species of philodendron vary. The ideal temperature for these plants is 60°F to 80°F, but they can still grow in temperatures as cool as 55°F. Providing the right temperature results in healthy growth and vibrant leaf color.
Philodendrons naturally thrive in moist conditions. With proper moisture management, plants experience healthy growth. Both excess and insufficient moisture can be harmful to plants. If proper humidity levels are not maintained, plant leaves may suffer from growth abnormalities. Too much moisture can cause root rot, which poses a risk to plant health. Generally, a humidity level of 60% to 70% is optimal for philodendrons.
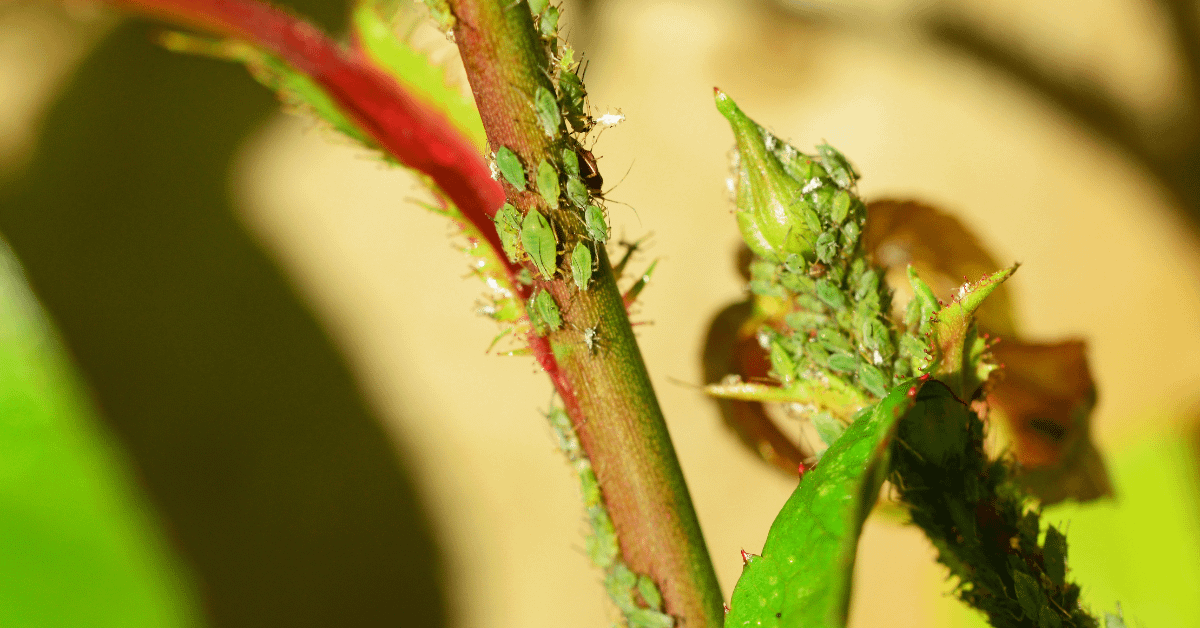
Pests Control
Indoor Philodendron plants are generally less prone to pests like cockroaches. However, they can attract mealybugs, spider mites, fungus gnats, aphids, bees, and whiteflies, which often hide under the stems or leaves. To manage these pests, you can use insecticidal soap mixed with water or neem oil, both of which are effective and less harsh on the plant. For severe infestations, a small amount of chemical spray might be necessary, but use it sparingly to avoid damaging the plant. Regular monitoring and maintaining good plant hygiene, such as removing debris and cleaning the leaves, can also help prevent pest issues.
Common Types Of Philodendron
Philodendrons, part of the Araceae family with around 450 species, are well-suited for indoor environments due to their low maintenance requirements. They thrive with optimal temperature, humidity, and care. Some common types include the heart-leafed Philodendron hederaceum, the large-leaved Philodendron bipinnatifidum, the deeply lobed Philodendron selloum, and the strikingly striped Philodendron Brasil. Each variety brings its own unique charm to indoor spaces. Below is a list of some common types of philodendrons:
Philodendron Brasil
Philodendron Brasil is a popular houseplant with vibrant heart-shaped leaves featuring green and yellow stripes. Growing 3 to 6 feet tall and 1 to 4 feet wide, it adapts well to various indoor spaces. Thriving in bright, indirect light and moderate humidity, it prefers well-draining soil and should be watered when the top inch of soil is dry. Minimal maintenance includes occasional pruning, leaf cleaning, and balanced fertilizer during the growing season.
Philodendron Birkin
Philodendron Birkin plants are extremely popular with gardeners for their attractive white and bright yellow variegated leaves. These plants thrive in indirect bright light and can grow slowly over time, making them ideal for small spaces. With proper care they can grow up to 3 feet tall. With a good potting mix, acidic soil, regular watering and minimal maintenance, these plants can be successfully grown indoors.
Philodendron Rojo congo
Philodendron Rojo congo is a spectacular species known for its unique red and green colors. This plant thrives in bright and indirect light, allowing its leaves to retain vibrant color. These plants can grow two to three feet tall and wide. With a good potting mix with moderate water, bright temperatures and warm humidity, growing Philodendron Rojo congo at home can be quite straightforward.
Heartleaf Philodendron
Heartleaf Philodendron is a popular species that can be easily grown indoors without much care. Its heart-shaped leaves and trailing vines, small white flowers and fragrant surroundings add to the beauty of the home environment. These plants usually grow like vines (3 to 12 feet tall and 1 to 3 feet wide). Providing bright light, a potting mix, water and the right temperature allows heartleaf philodendrons to thrive indoors with minimal maintenance.
Pruning Philodendron
Philodendrons are generally low-maintenance and do not require frequent pruning. However, occasional pruning can be beneficial for encouraging a more compact shape, promoting new growth, and maintaining overall plant health. If your Philodendron begins to outgrow its space or becomes leggy, pruning can help control its size and enhance its appearance.
When pruning, use a sharp, clean pruner or knife to make precise cuts, reducing the risk of disease or infection. Always make cuts just above a leaf node to encourage new growth. Besides shaping the plant, it’s important to remove any yellowing, damaged, or dead leaves and stems, as these can harbor pests or diseases that might spread if left unattended.
For larger Philodendrons, pruning can also involve cutting back some of the older, thicker stems to rejuvenate the plant. This stimulates the growth of new, vigorous shoots, keeping your plant lush and healthy. It’s best to avoid pruning during the winter months when the plant is dormant and not actively growing. Pruning during this time can stress the plant and slow its recovery. Instead, plan your pruning for the spring or early summer when the plant is in its active growth phase.
Propagating Philodendrons
The easiest method for propagating Philodendron plants is the stem cutting method. This technique allows you to easily grow new plants from an existing one. The ideal time for propagating Philodendron is at the beginning of spring. Below is the process for propagating Philodendron using the stem cutting method:
1. Select a Healthy Plant: Choose a mature Philodendron with healthy stems and leaves.
2. Take Cuttings: Using a clean, sharp knife or scissors, cut a 4-6 inch section of the stem just below a node (the point where leaves attach). Ensure the cutting has at least 2-3 leaves.
3. Prepare the Cuttings: Remove any leaves from the lower half of the cutting to prevent them from being submerged in water or soil, which can cause rot.
4. Rooting Medium: Propagate Philodendron cuttings in either water or soil. For water propagation, place the cuttings in a container of clean, room-temperature water, making sure the nodes are submerged. Change the water every few days. For soil propagation, plant the cuttings in a small pot with a well-draining mix of potting soil and perlite.
5. Provide the Right Conditions: Place the container in a warm, bright spot with indirect light. If propagating in water, cover the container with a plastic bag or a clear dome to maintain humidity. For soil propagation, keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy.
6. Wait for Roots: In water, roots typically develop within a few weeks. In soil, it may take a bit longer. Gently tug on the cuttings to check for resistance, indicating root growth.
7. Transplanting: Once the cuttings have developed a healthy root system, transplant them into individual pots with regular potting soil. Continue to care for them as you would for a mature Philodendron, providing adequate light, moisture, and temperature.
Potting And Repotting Philodendrons
Potting and repotting Philodendron plants are crucial for their health. When potting a new Philodendron, choose a pot with good drainage to prevent waterlogging. Use a well-draining potting mix, such as a blend of potting soil, perlite, and coconut coir, to ensure proper airflow and moisture control.
Repotting is typically needed every 1-2 years or when the plant outgrows its pot. At this time, select a pot slightly larger than the current one. Carefully remove the plant from its current pot, ensuring the roots are not damaged. Loosen any root tangles and trim off dead or excessively long roots. Place the plant in the new pot, add fresh potting mix, and lightly press it down. Water thoroughly to settle the soil and eliminate air pockets. After repotting, keep the plant away from direct sunlight for a few weeks to help it adjust to its new environment with less stress. After repotting, place the plant in a location with indirect light to help it adjust without the stress of direct sunlight. Monitor the plant for any signs of shock, such as wilting or leaf drop, and maintain consistent watering and humidity levels to support its recovery. Regularly check the soil moisture and adjust watering as needed to avoid overwatering or underwatering.
Common Problems With Philodendrons
Philodendrons can face issues such as yellowing leaves, which often indicate overwatering or inadequate drainage. Brown leaf tips are usually a sign of low humidity or underwatering. Leaf drop may result from sudden temperature changes or drafts. Regularly monitor watering practices and maintain appropriate humidity levels to keep your Philodendron healthy.
Yellow Leaves
Yellow leaves are a common problem in philodendron plants. Leaves can turn yellow for various reasons. If you use excessively cold water and place the plants in direct sunlight, the leaves may turn yellow. Additionally, if you apply too much water, the roots can rot, causing the leaves to turn yellow. To eliminate this problem, test your soil and water as needed, making sure to water at room temperature. Additionally, trim off yellowing leaves and consider applying some fertilizer.
Brown Leaves
If the leaves of your philodendron plant turn brown or have black spots, the likely causes are overwatering and direct sunlight. If you don’t incorporate perlite, peat moss, vermiculite, etc. into your soil and ensure proper drainage, water can accumulate at the plant’s roots, leading to root rot. Root rot can cause the main roots to die and the leaves to turn brown. Additionally, if you apply too much chemical fertilizer or spray chemicals, the leaves may turn brown or black. Therefore, to eliminate this problem, ensure a proper potting mix, adequate watering and minimal use of chemical fertilizers.
FAQ
How fast does Philodendron grow?
Philodendrons typically exhibit moderate to fast growth, often adding 12 to 24 inches of new growth per year under optimal conditions. They thrive in bright, indirect light with consistent watering and suitable humidity. With these ideal conditions, you can expect noticeable growth within a few months. However, growth may slow down in lower light or less favorable conditions. To support robust growth, ensure regular care, including appropriate fertilization.
Do Philodendrons clean the air?
Yes, Philodendrons are renowned for their air-purifying qualities. They can help remove indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, benzene, and trichloroethylene. Their broad, lush leaves absorb toxins and improve air quality by increasing humidity. To maximize these benefits, ensure the plant remains healthy with proper care, including adequate light, consistent watering, and occasional dusting of the leaves.
Do all Philodendrons need the same care?
While many Philodendrons share similar care requirements, specific needs can vary by species. Most prefer bright, indirect light, moderate humidity, and well-draining soil. However, some varieties may tolerate lower light or drier conditions better than others. It’s important to research the specific needs of your Philodendron species to ensure optimal growth and health. Tailoring care to each plant’s requirements will help maintain their vitality and appearance.