The lucky bamboo is actually not bamboo at all; its scientific name is Dracaena sanderiana, and it belongs to the Asparagaceae family. It is extremely popular among gardeners because it is easy to grow and requires minimal maintenance. It is believed to represent good luck and happiness. Another reason for the popularity of lucky bamboo is its twisted or woven stems and other decorative shapes. These forms can be trained to grow in such a way that the stems become arrow-straight and adorned with small, simple leaves. Lucky bamboo typically grows quickly like bamboo and can enhance the beauty of homes and offices with minimal care. However, this plant is generally toxic to pets such as dogs and cats.
How To Grow For Lucky Bamboo
Lucky bamboo is highly popular for its attractive beauty in homes, offices, and restaurants. These plants are typically hardy and require minimal maintenance. With proper well-draining soil, indirect bright light, optimal temperature, moderate water, correct humidity, and minimal supervision, they can easily thrive. These plants are capable of adding an aesthetic touch to the environment of a home. Below are some guidelines for growing lucky bamboo at home:
Light & Location
Lucky bamboo generally prefers moderate to low indirect light. It does not thrive in direct sunlight, as exposure to direct sunlight can cause the leaves of the plant to scorch and may lead to less growth than necessary. Different species of lucky bamboo may have varying requirements for light. For optimal growth, you can place your plant near a medium-bright window (preferably in the south-east corner) where it receives indirect sunlight. Be mindful to avoid direct sunlight falling on your plant. Additionally, you can grow lucky bamboo plants in living rooms, office spaces, and bathrooms. With adequate but not excessive light, your plants will receive the proper amount of light needed for their leaves to grow properly and remain vibrant.
Soil & Fertilizer
Generally, lucky bamboo does not require soil for growth. However, since it is often used for enhancing the beauty of indoor spaces, soil is sometimes used for aesthetic purposes and root growth. Using soil with good drainage is ideal for lucky bamboo. In this case, a mix of potting mix with vermiculite, perlite, coco coir, and dry bark pieces helps provide a good drainage system for the soil.
Lucky bamboo does not typically require fertilizers. However, if you want your plants to grow, have lush leaves, and remain vibrant, you can add liquid fertilizer once a month during the growth seasons. Be cautious about applying fertilizer in the winter season. Over-fertilizing your plants can lead to leaf burn and stunted growth, so it’s best to apply fertilizer as needed.
Watering
Lucky bamboo is primarily cultivated using the hydroponics method, though it is also often grown in soil. If you are growing your plants in water, ensure a continuous supply of water for 24 hours. Avoid using water containing chlorine and other chemicals, as these can be harmful to lucky bamboo. In the hydroponics system, you can use pure, room temperature water. Replace the water every two to three days and change it completely every 7 to 15 days. If you prefer to grow lucky bamboo in soil, provide moderate amounts of water to the plants. Overwatering can cause the leaves to droop, roots to rot, and lead to root decay. Therefore, check if the soil is dry and water as needed, typically once or twice a week. Regular watering will help maintain the proper growth and vitality of your plants.
Temperature & Humidity
Lucky bamboo prefers moderate to warm temperatures. The ideal temperature range for lucky bamboo plants is between 60-90°F. For indoor growth, you can place the plant in a shaded area, maintaining the proper temperature with minimal care. If you have an air conditioner or heater at home, keep the plants away from these devices.
Lucky bamboo plants prefer bright to moderate humidity. Typically, you don’t need to use a humidifier or spray water to increase the humidity for these plants. They thrive best in household humidity levels ranging from 40%-60%. If the humidity in your home drops significantly, you can place the plant on a tray filled with water and surrounded by pebbles. This will allow the water to evaporate and increase the humidity around the plant.
Pests Control
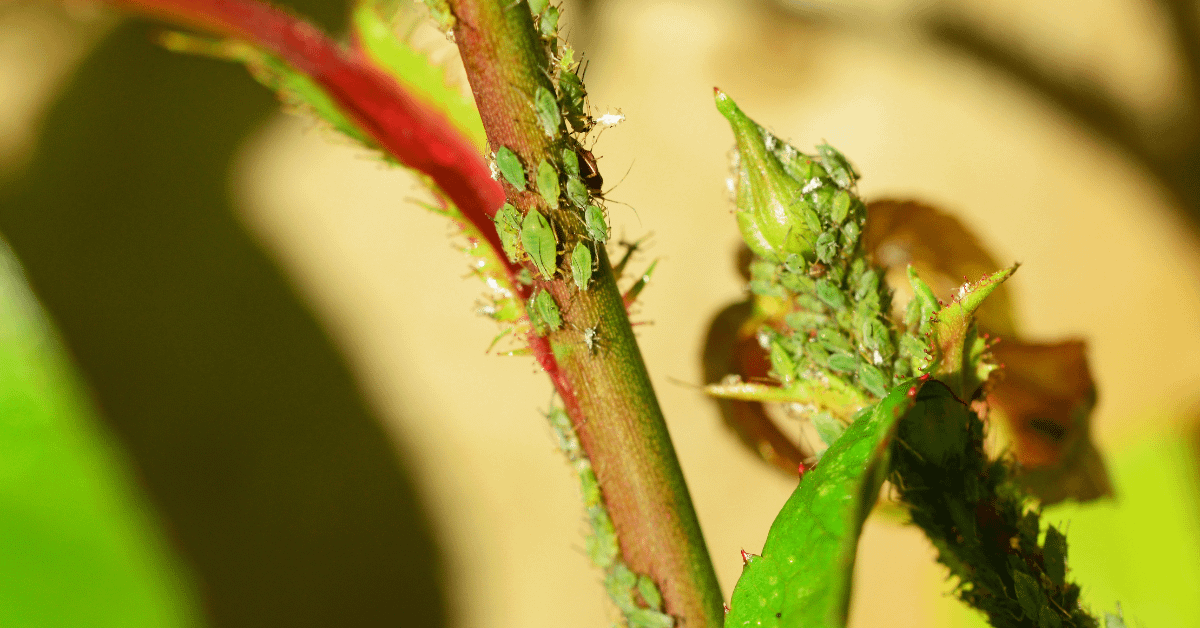
Lucky bamboo is also susceptible to insect infestations as other houseplants. Mealybugs, spider mites, aphids, scale, and whiteflies are some of the pests that can attack lucky bamboo plants. These insects sit on the stems and suck the sap, and they can also be found under the leaves, feeding on them. To get rid of these pests, you can use a spray of soapy water, neem oil, or apply alcohol to the plant. Additionally, if the infestation is severe, a small amount of chemical spray can be used, but excessive use can be harmful to the plant.
Pruning
Lucky bamboo plants typically experience rapid growth, whether at home, in the office, or in restaurants, as they are cultivated for ornamental purposes. Therefore, when the plants undergo excessive growth, it can detract from the indoor aesthetic. Thus, regular pruning is necessary to maintain the proper shape of the plants. In general, it’s not advisable to cut the main stalk of lucky bamboo. Instead, trim the offshoots and cut them back to within an inch or two of the main stem. New offshoots will soon emerge from the cut section. Additionally, if any part of your plant is damaged, it can also be trimmed using a sharp pair of scissors or pruners.Regular pruning encourages the growth of new shoots and revitalizes the plants’ vitality.
Propagating Lucky Bamboo
Propagation of lucky bamboo is very easy and can be done at any time of the year using cuttings. The propagation methods for lucky bamboo are outlined below:
- Cutting the Stem: Select a healthy and long lucky bamboo stem that is thick and strong, with at least one or two nodes (where the leaves are attached). Cut a section of the stem about 2-3 inches long.
- Preparing the Cutting: Keep the cut end of the stem clean and intact. Place this end in water for a while to start developing new roots.
- Placing in Water: Immediately after cutting, place the lower part of the stem in water. Ensure that the water level is such that only the node area is submerged, and the cut end remains above the water.
- Maintenance: Regularly check the water level and change the water as needed. Typically, water should be changed every 7-10 days to aid in the formation of new roots.
- Care: Once new roots have developed, the stem can be transferred to a new container. It can be placed in soil or pebbles, but lucky bamboo generally thrives well in water.
Potting & repotting Lucky Bamboo
Lucky bamboo can be grown in various ways, such as using soil-based and hydroponic methods. Both methods are highly effective for growing lucky bamboo. For the soil-based method, choose a pot with proper drainage holes according to the size of your plant and fill it with a fertile potting mix. Place your plant in the pot, add fertilizer and water, and press the soil firmly with your hands.
On the other hand, the hydroponic method involves growing plants in water without using soil. For the hydroponic system, select a container according to the size of your plant and add a layer of vermiculite, peat moss, perlite, and pebbles. Now place your lucky bamboo plant in the container. Then add pure, room temperature water and set up an air pump if desired.
Soil-Based System
In many cases, gardeners prefer to grow lucky bamboo in a pot using soil. Lucky bamboo can grow very quickly, so you may need to repot your plant within 1-2 years. When you notice that your plant has grown significantly and is outgrowing its pot, you can repot the plant using a new pot and growing medium.
Choose a pot with proper drainage holes according to the current size of your plant, and select a suitable potting mix that includes organic materials like vermiculite, perlite, and peat moss. Add the potting mix to the new pot, and carefully remove the plant from the old pot, keeping the roots intact. Place the plant in the new pot, add water, fertilizer, and more potting mix, and press the soil firmly with your hands.Then, move your plant to a bright, shaded area and provide the necessary care to help it regain its vitality. Always repotting during the growing season and avoid repotting in the winter.
Hydroponic System
Lucky bamboo is often grown using hydroponic systems, which is a modern indoor gardening method that utilizes water and other nutrients instead of soil to support plant growth. Since lucky bamboo is a fast-growing plant, it may need repotting within 1-2 years.
For repotting, select a glass or plastic container based on the current size of your plant. To ensure proper drainage, you can add materials like vermiculite, perlite, peat moss, coco coir, along with stones to the container. Then carefully transfer your plant from the old pot to the new one, ensuring that the roots are intact. In hydroponic systems, since the plant’s roots are directly submerged in water, you can add an air pump system to provide oxygen to the roots.
Since plants in hydroponic systems can grow rapidly, it’s important to choose plant varieties that are comfortable with nighttime conditions. Once the repotting process is complete, keep your plant in a bright, sunny location and provide necessary nutrients to support its growth.
Common Problems With Lucky Bamboo
Lucky bamboo plants can grow very rapidly with minimal care, but they may encounter several issues during their growth period. These issues include yellow leaves, blocked roots, algae growth, and fungal infections. These problems can arise for various reasons, such as overwatering, excessive sunlight exposure, and over-fertilization. Here’s a detailed discussion of these problems and their solutions:
Yellow & Brown Leaves
Yellow or brown leaves on lucky bamboo are a common issue. The leaves of lucky bamboo can turn yellow or brown for various reasons, such as overwatering, direct sunlight, and over-fertilization. Lucky bamboo prefers bright, indirect light, but if the tips are exposed to direct sunlight, the leaves can scorch and turn yellow or brown. Therefore, choose a shaded location for the plants or use a light-filtering arrangement. Overwatering, chlorine, and chemical-laden water can be sensitive to the plant, causing root rot and yellowing leaves. To prevent this issue, use pure water at room temperature and check the soil before watering to ensure it is necessary. Additionally, in a hydroponic system, change the water in the container every 7 to 15 days.
Black Roots
Blackening of the roots in lucky bamboo can be a severe issue, commonly occurring in hydroponic systems. If this problem arises, immediately use a small, sharp pair of scissors or pruners to cut off the affected roots and transfer the plants from the old container to a new one with pure and clean water. Delaying can worsen the disease, leading to the plants’ gradual death, so taking prompt action is crucial.
Algae
Lucky bamboo plants in a hydroponic system can be affected by algae. Usually, if you have a transparent container and direct sunlight enters the container, it promotes algae growth. To remedy this issue, clean the container thoroughly and restart the hydroponic system. If algae remains a persistent problem, grow your plant in an opaque container, which reduces sunlight penetration and inhibits algae growth.
FAQ
Do lucky bamboo grow in water?
Yes, lucky bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana) can thrive in water. To grow it successfully, place the plant in a container filled with enough water to cover and submerge the roots. Change the water every 2-4 weeks to prevent stagnation and algae growth. Provide indirect light and occasionally add liquid fertilizer to support healthy growth. Keep the water level consistent and avoid direct sunlight.
Can lucky bamboo grow outdoors?
Lucky bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana) is primarily an indoor plant due to its sensitivity to temperature and light conditions. It can grow outdoors in warm, shaded areas with indirect light, but it’s not frost-tolerant and should be protected from direct sunlight and cold temperatures. For successful outdoor growth, ensure it’s placed in a sheltered location with consistent moisture and avoid extreme weather conditions to keep the plant healthy.