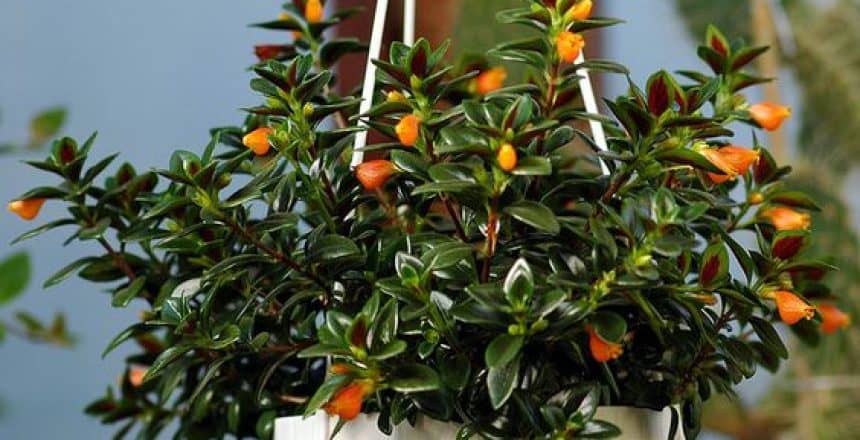
The scientific name of the goldfish plant is Nematanthus gregarius. Goldfish plants are popular among gardeners and beauty enthusiasts for their bright orange flowers that resemble the fins of a swimming goldfish. The leaves of goldfish plants are smooth and finely arranged, almost completely green, making them ideal for making beautiful hanging baskets and adding a splash of color to any room and doubling the beauty of the home. These plants are usually two to three feet tall and about two feet wide, bearing red, orange, yellow and pink flowers. With proper care, including adequate warmth, bright indirect light, well-drained acidic soil, and moderate watering, goldfish plants can thrive indoors.
How To Grow Goldfish Plant
Taking care of goldfish plants is easy and manageable, making them suitable for cultivation in homes with minimal effort. Goldfish plants are native to the tropical regions of Central and South America, preferring high humidity and bright indirect light. They can be grown both indoors and outdoors. Providing moderate watering, bright light, slightly acidic, nutrient-rich soil, and the right mix, goldfish plants can easily thrive indoors. Here are some essential tips for growing a goldfish plant:
Location & Sunlight
Goldfish plants prefer bright, indirect light. They typically require this lighting condition for around 6-8 hours a day. However, they do not thrive in direct sunlight as it can scorch their leaves. To provide adequate indirect light, it’s essential to choose a suitable location for them. You can opt for north or east-facing windows, and if direct sunlight reaches them, you can use a sheer curtain to filter the light. If you notice your goldfish plants aren’t flowering enough, you can move them to a brighter location. Additionally, if your home lacks natural light, you can implement a grow light system to ensure the plants receive sufficient illumination.
Soil & Fertilizer
For goldfish plants, it’s ideal to use well-draining, high-quality potting soil or a succulent soil mix with good drainage. Mixing heavy clay soil with materials like perlite, vermiculite, pumice, or coco coir aids in drainage and promotes healthy root development. Additionally, slightly acidic soil with a pH of 5.5-6 can be beneficial for goldfish plants.
Fertilizing goldfish plants is essential. During the growing season, fertilize the plants every two weeks, and reduce fertilization during the winter months. Before applying fertilizer, moisten the soil, and then apply it to damp soil. You can try using compost fertilizer, and if that’s not available, you can use a small amount of chemical fertilizer following the instructions on the packet. Proper fertilization helps in abundant flowering and overall health and vitality of goldfish plants.
Watering
Providing regular water to goldfish plants is an integral part of their care. When you notice the top layer of soil in your pot has dried out, it’s time to water them. During the growing season, plants require more water, so apply a measured amount of water to keep the soil lightly moist, ensuring proper drainage holes in the pot. In winter, reduce watering, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot. Adequate water helps promote flower production for goldfish plants.
Temperature & Humidity
The ideal temperature range for goldfish plants is between 65°F and 75°F. Extreme temperatures can cause issues such as leaf burn in high temperatures or hindered flower production in excessively low temperatures. Therefore, keep your plants in a bright location where they can receive sunlight if necessary.
Maintaining proper humidity levels is crucial for the healthy growth of goldfish plants. They prefer a high humidity level ranging from 50% to 80%. During the winter when indoor humidity decreases, you can increase humidity levels for your plants by using a small humidifier or incorporating other humidity-boosting elements. Additionally, to maintain healthy humidity levels, you can place a pebble and water-filled tray beneath the plant’s pot, allowing the water to evaporate and increase humidity around the plant’s foliage.
Pests Control
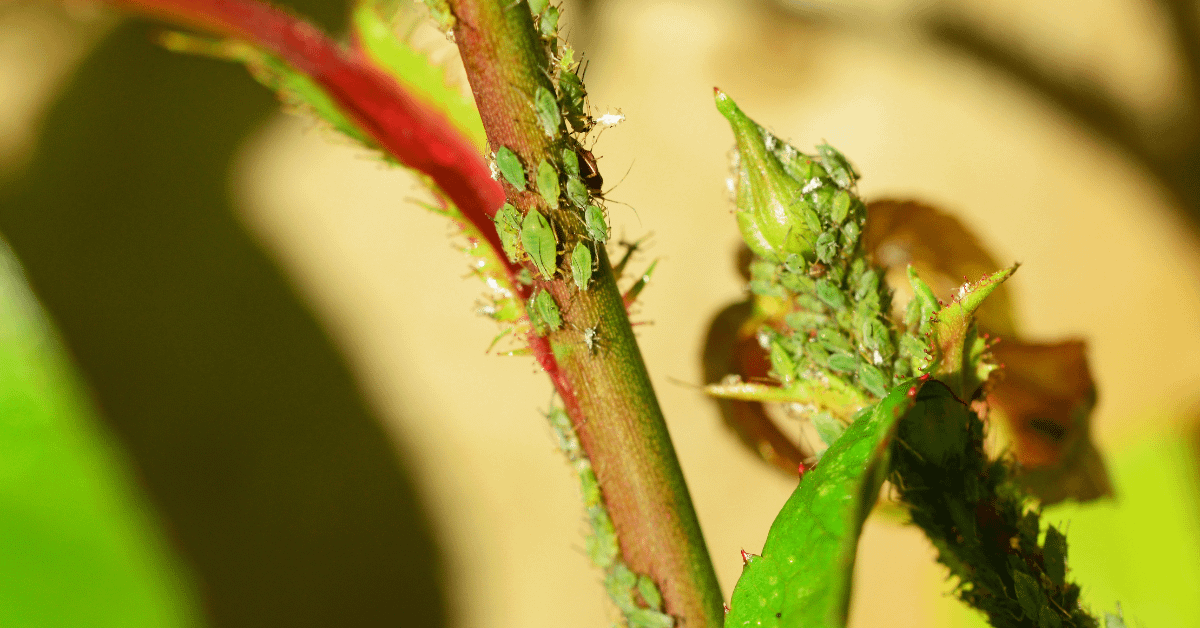
Goldfish plants are generally less prone to pest infestations. However, aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs can pose a threat to your goldfish plant. Aphids and whiteflies suck the sap of the plant and can hinder its growth, while mealybugs typically feed on the undersides of leaves, causing them to wilt. Additionally, goldfish plants can be susceptible to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and gray mold.To combat these issues, you can use insecticidal soap spray or neem oil spray on your plants. For severe infestations, you may need to resort to chemical sprays, but use them sparingly and according to the instructions.
Types Of Goldfish Plants
The Goldfish plant is categorized into two genera: Columnea and Nematanthus, each featuring various cultivars and hybrids. Columnea includes species like Columnea gloriosa with vibrant orange blooms, while Nematanthus has varieties such as Nematanthus wettsteinii, known for its bright red or yellow flowers. Both genera are valued for their unique floral displays and trailing growth habits.
Tropicana
Tropicana is a cultivar of the goldfish plant (Nematanthus) renowned for its lush green foliage and vibrant, fish-shaped flowers. The blooms are bright red with striking orange stripes, resembling goldfish. This cultivar thrives in well-draining soil, with regular watering, moderate temperatures, and bright, indirect light. It is an easy plant to grow, making it a favorite for home gardens.
Green Magic
Green Magic is a distinctive variety of the goldfish plant (Nematanthus), known for its rich green leaves and bright orange flowers. Its unique growth habit and striking color contrast make it highly desirable. It thrives in bright light and well-draining potting mix, with moderate watering and high humidity. Proper fertilization and care are essential for maintaining its vibrant appearance.
Black Gold
The Black Gold variety of the goldfish plant (Nematanthus) is distinguished by its dark green foliage with red highlights and vibrant orange flowers. This contrast adds a dramatic effect to its appearance. It prefers bright light, acidic soil, and consistent watering. With proper care, it remains a visually stunning addition to any plant collection.
Light Prince
Light Prince, a variety of Columnea hirta, is celebrated for its white and green variegated leaves and vibrant orange-yellow flowers. It grows to a height of 8 to 12 inches with a spread of 12 to 18 inches and can be shaped through regular pruning. This variety is relatively easy to care for, thriving in bright, indirect light and adding a splash of color to indoor spaces.
Pruning Goldfish Plant
Pruning goldfish plants is essential for their health, vitality, and appearance. Regular pruning encourages new growth and helps the plant develop fresh shoots. To maintain a desired shape or compactness, periodically prune the stems and leaves. Removing dead or damaged parts is crucial, as they can affect the plant’s health and appearance. Use sharp, sterilized pruners or scissors to make clean cuts, which prevents disease and promotes quicker healing. Pruning after the blooming period allows the plant to focus its energy on new growth and prepare for the next flowering cycle. By following these practices, you ensure that your goldfish plant remains robust, well-shaped, and vibrant.
Propagating Goldfish Plant
Although propagating Goldfish plants from seeds is not recommended due to its difficulty, especially outside their natural habitat, stem-tip cuttings are a more effective method. Here’s how to propagate Goldfish plants using cuttings:
- Choose healthy stems from the Goldfish plant, ideally 4-6 inches long, with a few leaves. Ensure the stems are not too young or too old.
- Trim the leaves from the lower half of the cutting and dip the cut end in rooting hormone to promote root growth.
- Place the cuttings in a pot with a well-draining soil mix, such as a blend of perlite and peat moss. Make a hole in the soil and insert the cutting.
- Cover the pot with a plastic bag or a clear dome to maintain high humidity, which helps the cutting develop roots.
- Place the pot in bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can be too intense for new cuttings.
- Keep the soil lightly moist but not soggy. Allow the top layer of soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
- After a few weeks, check for root development by gently tugging on the cutting. Once roots are established, transplant the new plant into a larger pot or directly into the garden.
Potting And Repotting Goldfish Plant
Repotting Goldfish plants should generally be done every one to two years or when you notice the plant’s growth slowing down or the roots growing out of the drainage holes. The best time for repotting is during the growing season, typically at the beginning of spring or summer. Avoid repotting in winter, as the plant is less active and may experience additional stress.
To repot, select a new pot that is 1-2 inches larger in diameter than the current one and has good drainage. Lightly water the plant to make removal easier. Gently remove the plant from its old pot, loosen any bound roots, and trim away any damaged or excessively long roots. Place the plant in the center of the new pot, adding fresh potting mix around the root ball. Ensure the plant is at the same depth as it was in the old pot. Lightly press the soil to remove air pockets without compacting it too tightly. Water the plant thoroughly to help settle the soil. After repotting, place the plant in a bright, indirect light location. Avoid fertilizing for a few weeks to allow the plant to adjust to its new pot, and monitor for any signs of transplant shock.
How To Get Goldfish Plant To Bloom
The Goldfish plant blooms in spring, summer, and fall, and may enter a near-dormant state in winter, although it can still produce some flowers. To encourage blooming, provide the plant with bright, indirect light, as direct sunlight can reduce flower quality. Ensure the soil is well-draining, using a mix such as peat moss, perlite, and pine bark. Feed the plant with a diluted fertilizer once a week or every other week, choosing a phosphorus-rich fertilizer during the blooming period. Remove spent flowers to promote new blooms. Keep the plant at a temperature of 60-75°F (15-24°C), as colder temperatures can reduce flower production. Maintain proper humidity, as the Goldfish plant prefers high humidity. Increase humidity through regular misting or by using a humidifier.
Common Problems With Goldfish Plants
Goldfish plants are relatively easy to grow at home with minimal maintenance, but they can encounter some issues. Common problems include yellow leaves, curling leaves, and leggy growth. These issues are often caused by overwatering, excessive sunlight, and insufficient humidity. Identifying these problems and taking the appropriate measures can help resolve them. Below is a discussion of these common issues and their solutions for Goldfish plants:
Leggy Growth
Goldfish plants typically prefer bright light, high temperatures, and moderate watering. However, if they receive excess water and lack proper light, they may develop leggy growth. Therefore, it is important to prioritize providing these plants with bright light and to use a high-quality potting mix with advanced drainage capabilities.
Browning Leaves
Goldfish plants prefer high temperatures, high humidity, and bright but indirect light. However, if they are directly exposed to sunlight, their leaves may scorch and turn brown, and the plants may experience stunted growth. Therefore, when placing the plants outdoors, it’s essential to position them in a brightly shaded area rather than under direct sunlight. Alternatively, if you want to grow them indoors, you can place them on a windowsill facing north or west and use an arrangement to filter direct sunlight for protection.
Curling Leaves
Goldfish plants typically thrive in warm, tropical climates, so it’s crucial to provide them with the right amount of water. If your plants experience drought, their leaves may curl, and flower production may decrease. Additionally, even exposure to direct sunlight can cause leaf curling. To address these issues, consistent watering, providing bright light, and regularly spraying water to increase humidity are necessary.
FAQ
Can you grow a goldfish plant outdoors?
Goldfish plants (Columnea) can be grown outdoors in warm climates where temperatures consistently stay above 50°F (10°C). They prefer shaded or partially shaded areas to avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch their leaves. Ensure the soil has good drainage and avoid overwatering. In cooler climates, it’s best to keep them indoors or move them indoors during colder months to protect them from frost and low temperatures.
Can I grow goldfish plants from seed?
Yes, you can grow Goldfish plants (Columnea) from seeds, though it requires patience. Start seeds in a well-draining seed-starting mix and maintain a warm, humid environment with indirect light. Germination can take several weeks. Once seedlings are large enough, transplant them into larger pots with a mix of potting soil and perlite. Proper care and maintenance will support their healthy growth and development.